Receiving a warning letter from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is regarded as a significant concern. It indicates that FDA finds regulatory non-compliance with the company’s practices, and may take actions if the issues are not promptly addressed.
This report serves as a proactive practice for the pharmaceutical industry, analyzing trends of the most recent FDA citations and warning letters related to drug category, based on publicly available data on FDA’s official website for FY 2022 and FY 2021.
The purpose of this analysis is to categorize and breakdown the findings identified by the FDA during drug production, delving into the underlying reasons behind these categories. By undertaking such analysis, we aim to shed light on the extent to which these findings can be minimized or eliminated altogether through the implementation of digitalization.
The Analysis of FDA’s Citations and Warning Letters
Let’s dive into the FDA inspections conducted in FY 2021 and FY 2022, focusing on the citations and warning letters issued during this period.
- In FY 2022, FDA conducted 1175 inspections and issued 1469 citations. Compared to FY 2021, there was approximately a 31.14% increase in the number of inspections and 55.12% increase in the number of citations.
- The number of inspections in the US showed a significant increase from 730 in FY 2021 to 840 in FY 2022, representing a 15.1% increase.
- The number of inspections outside of the US experienced a remarkable surge from 158 in FY 2021 to 352 in FY 2022, showcasing a 122.8% increase.
By examining the most common reasons for citations and warning letters, we observed a remarkable similarity between the two. A significant proportion of these findings were related to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) in FY 2022, highlighting the FDA’s emphasis on written procedures and quality systems.
Top 10 Most Frequently Cited Violations: Findings from FDA Citations
In FY 2021, the highest number of citations were given to “Bioresearch Monitoring-21 CFR 312.60-FD-1572, protocol compliance,” with a rate of 17.9%. Additionally, in FY 2021, the citation “Drugs-21 CFR 211.22(d)-Procedures not in writing, fully followed” closely followed with a rate of 17.3%.
The table provides an overview of the most frequently cited issues related to drug manufacturing regulations and highlights the areas where compliance problems were most prevalent in FY 2022. The FDA issued 1469 citations during this year, with the highest number of citations (103, %22.5) given for Drugs-21 CFR 211.22(d)-Procedures not in writing, fully followed. Additionally, the other given citations are due to incompatibility with the clauses in the title Drugs-21 CFR 211, which fall under GMP regulations.
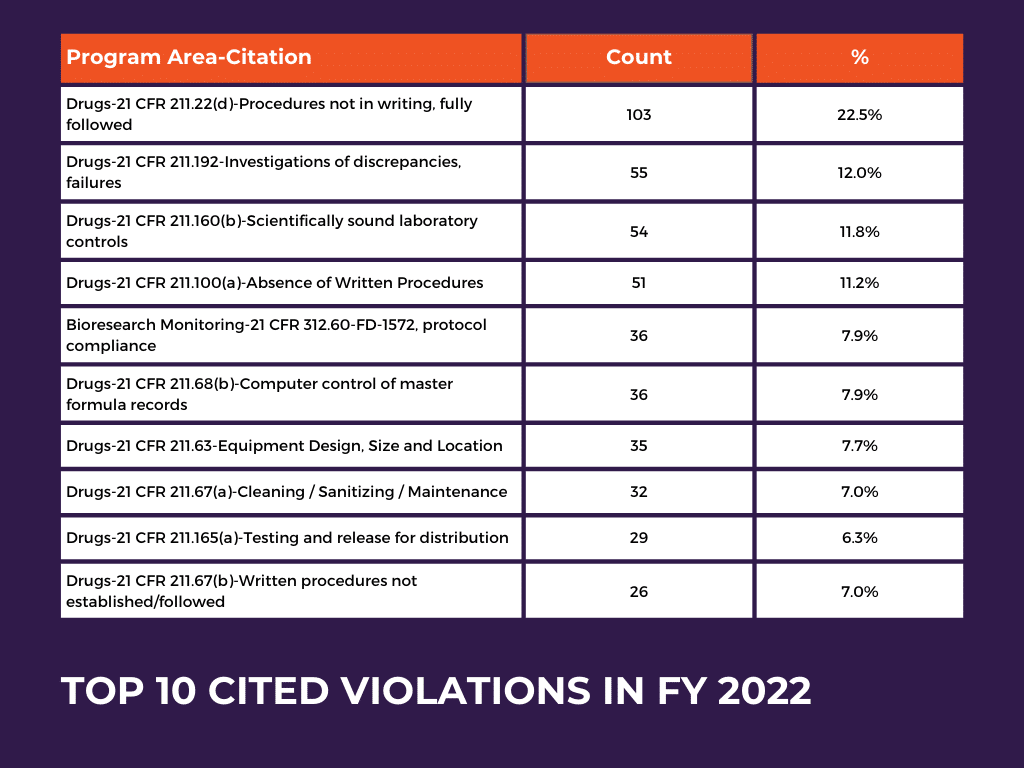
The increase in citations in the Drugs-21 CFR 211.22(d) category from 17.3% in FY 2021 to 22.5% in FY 2022 signifies a noteworthy escalation and highlights the importance of addressing this particular compliance challenge.
GMP-Related Warning Letters: A Closer Look at Key Findings
In FY 2021, 27 GMP-related warning letters were issued, accounting for 17.3% of the total warning letters (156) sent out for drug-related issues.
In FY 2022, there was a notable increase in the percentage of GMP-related Warning Letters. Out of the total 149 drug warning letters issued, 42 were specifically related to GMP issues, representing 28.2% of the overall warning letters sent out. To gain deeper insights into the role of GMP regulations in these warning letters, let’s examine the table below. This table presents an overview of the most frequently received warning letters concerning drug manufacturing GMP regulations.
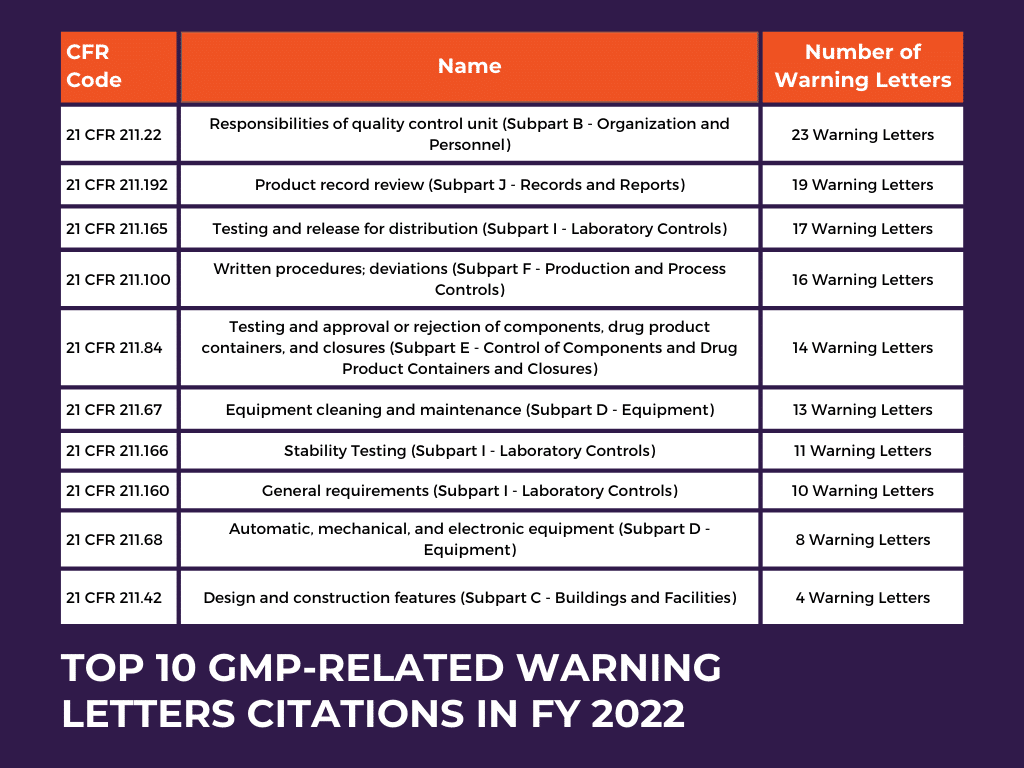
Among the warning letters issued by the FDA, two key violations stand out as the most frequently cited reasons related to GMP regulations. These violations fall under ’21 CFR 211.22 Responsibilities of quality control unit (Subpart B – Organization and Personnel)’ and ’21 CFR 211.100 Written procedures; deviations (Subpart F – Production and Process Controls).’
Let’s look into the specific reasons that have been identified as major contributors to the issuance of warning letters in these areas: (Furthermore, the corresponding sections of 21 CFR Part 211 for these reasons behind receiving these warning letters are also indicated alongside)
- Batch documentation and batch release undergo a Quality Assurance (QA) review. (Related 21 CFR 211.188 Batch production and control records)
- QA releases batches without proper validation of the testing methods. (Related 21 CFR 211.160 General requirements)
- Batches are released by QA before conducting a review of manufacturing documentation. (Related 21 CFR 211.192 Production record review)
- The Quality Unit’s responsibilities towards contract manufacturers and laboratories are not outlined in any quality agreements. (Related 21 CFR 211.22 Responsibilities of quality control unit)
- The contract manufacturer lacks a release procedure for starting materials or components used in product manufacture. (Related 21 CFR 211.80 General requirements)
- QA fails to ensure that the test methods of the contract laboratory are properly validated. (Related 21 CFR 211.194 Laboratory records)
- Procedural instructions for critical GMP-related processes are missing, including batch release, quality-critical manufacturing processes, operation of production equipment, deviation clarification in the laboratory (OOS results), microbiological tests on the product, implementation of CAPAs, handling of complaints, returns, and recalls, evaluation of changes, ongoing stability tests, and annual product review. (Related 21 CFR 211.100 Written procedures; deviations)
- Lack or inadequacy of written procedures,handling of deviations,product quality issues, inadequate recordkeeping and reporting, training and personnel competence. (Related 21 CFR 211.192 Production record review, 21 CFR 211.198 Complaint files )
The most frequently cited reasons for FDA warning letters reveal crucial areas where pharmaceutical manufacturers need to enhance their compliance to GMP regulations. Manual processes, insufficient tracking systems, ineffective monitoring mechanisms, and the absence of written procedures are some of the critical factors contributing to the risk of receiving warning letters.
In order to guarantee consistency, accuracy, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) written procedures are needed by the FDA. These procedures serve as a critical tool to guide and standardize the activities within a Pharmaceutical Plant. FDA expects the Quality Unit to play a central role in ensuring the compliance and quality of pharmaceutical products.
Pharmaceutical companies can mitigate the risk of non-compliance, enhance product quality, and maintain a strong reputation within the industry by addressing these issues and prioritizing improvements in these areas.
You can read our “In-depth Guide to cGMP: Definition, Importance & Best Practices” article to learn more about Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP).
The Roadmap to FDA Approval: Embracing Digitalization in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The pharmaceutical industry’s examination of FDA citations and warning letters has highlighted important compliance issues and suggestions for improvement. Given the sharp rise in GMP warning letters and citations, it is obvious that adherence to GMPs is crucial for pharmaceutical companies seeking FDA approval.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing plants can succeed in FDA inspections by utilizing digital manufacturing solutions such as our Digital Logbook to address the requirements of FDA 21 CFR Parts and prevent potential issues. Manufacturers can standardize processes by using these digital solutions, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and regulatory compliance. Notably, the digitalization of logbooks, and batch records stand out as the most effective solution for pharmaceutical manufacturers, enabling them to comply with FDA 21 CFR Parts standards.
Transferring manual processes to a digitalization offers several benefits:
Digital Transformation: Reducing paper usage makes your business more open to digitalization. This enables you to adapt more quickly to future technological developments.
Data Security: Digitalization can help you better secure your data. Security measures such as encryption and authorization keep your data safer.
Compliance and Standards: Digitalization can be more flexible in complying with specific industry standards or regulations. You can quickly implement changes when needed.
Time and Efficiency Increase: With digitalization, data entry becomes faster and easier. It reduces the time required for organizing, storing, and searching for manual documents.
Easy Access and Sharing: Digitalization allows access to data from anywhere and any device, facilitating collaboration and data sharing among teams.
Reporting and Analysis: Digitalization is more conducive to analyzing and reporting data. Having more data allows you to evaluate and improve process performance.
Organization and Structure: Digitalization helps maintain data in an organized and easily searchable manner. Search and filtering options enable quicker document retrieval.
Cost Savings: Reduced paper, printing, and storage costs can lower your overall business expenses.
Reduced Physical Space Usage: Less need for paper document storage can lead to more efficient office space utilization.
Environmental Sustainability: Decreasing paper usage contributes to reducing environmental impacts, aligning with sustainability goals.
With the digitization of processes, certain findings related to specific CFR 21 Part 211 sections may have been avoided as can be seen below:
- CFR 21 Part 211.100 – Written Procedures: Digitization can aid in easier monitoring and documentation of process adherence to written procedures.
- CFR 21 Part 211.22 – Responsibilities of Quality Control Unit: Digitization can help streamline the responsibilities of the quality control unit, making it easier to monitor and ensure compliance with established quality standards and procedures.
- CFR 21 Part 211.160(b) – Equipment Cleaning and Maintenance: Digitization can be instrumental in ensuring compliance with CFR Part 211.160(b) regarding equipment cleaning and maintenance. By implementing digital systems, the company can establish automated tracking of equipment cleaning schedules, maintenance activities, and associated documentation.
- CFR 21 Part 211.122 – Materials Receipt, Handling, Storage, and Issuance: Digitization can streamline tracking and management of material receipt, handling, storage, and distribution.
- CFR 21 Part 211.134 – Drug Product Inspection: Digitization can enhance visual inspection and control of drug products.
- CFR 21 Part 211.186 – Master Production and Control Records: Digitization can facilitate the management and documentation of production and control records.
- CFR 21 Part 211.192 – Production Record Review: Digitization can make the review and approval of production records more efficient and reliable.
- CFR 21 Part 211.194 – Laboratory Testing: Digitization can support effective planning, execution, and management of laboratory testing and results.
- CFR 21 Part 211.67(b) – Equipment Cleaning and Use Log: Digitization can streamline compliance with CFR Part 211.67(b), which pertains to maintaining an equipment cleaning and use log. Through digital solutions, the company can establish electronic logs that automatically record equipment cleaning, usage, and related activities.
This implies that if pharmaceutical companies choose to digitize their operations, they could potentially avoid approximately 289 out of the total 457 top 10 citations issued in FY 2022. Furthermore, digitalization might have the potential to prevent as many as 71 out of the 135 warning letters received, as indicated in the Top 10 Warning Letters of 2022.

