The pharmaceutical industry, a cornerstone of global health, stands at a critical juncture. The recent political landscape in the United States, marked by a Republican majority in both the Senate and the House of Representatives, and the re-election of Donald Trump, signals a potential paradigm shift in economic policy. Trade tariffs, the focus of renewed emphasis, possess the power to reshape the pharmaceutical manufacturing sector, both domestically and internationally.
This is not simply a continuation of past trade disputes. While tariffs were a feature of the first Trump administration and continued to some extent under President Biden, their scope and intent have evolved significantly. What was once largely focused on addressing perceived trade imbalances with China has now broadened to encompass long-standing U.S. trade partners, including Canada, Mexico, and European nations. This expansionary approach demands a new level of understanding and strategic adaptation from pharmaceutical manufacturers.
The implications of Trump Tariffs are far-reaching. From potential supply chain disruptions to pricing pressures, from reshoring opportunities to the further incentive for Pharma 4.0 transformation, the future of pharmaceutical manufacturing is being actively reshaped. To help pharma professionals, consultants, and policymakers navigate this complex environment, we have written this article. A more comprehensive and detailed version is also available in our free eBook format. This PDF version provides in-depth pharmaceutical trade data analysis, extended actionable strategies, and more detailed guidance to equip you to thrive in this evolving landscape.
Understanding the Trump Tariff Landscape
To grasp the potential impact of these policies, it is crucial to understand the current tariff landscape. The Trump administration’s “America First” policy prioritizes trade reciprocity, meaning a balanced exchange of goods between the U.S. and its trading partners. This principle is driving the implementation of tariffs as a tool to achieve this balance.
The tariff landscape for pharma industry can be broadly categorized as:
- Publicly Targeted Countries or Regions: These are countries or regions that have been publicly identified as potential tariff targets through executive orders, White House statements, presidential speeches, and official social media posts. These pronouncements create uncertainty and require careful monitoring.
- Implemented Tariffs: This category refers to tariffs that have already been officially enacted, affecting specific sectors or products, including pharmaceuticals. These tariffs have immediate and measurable consequences for the industry.
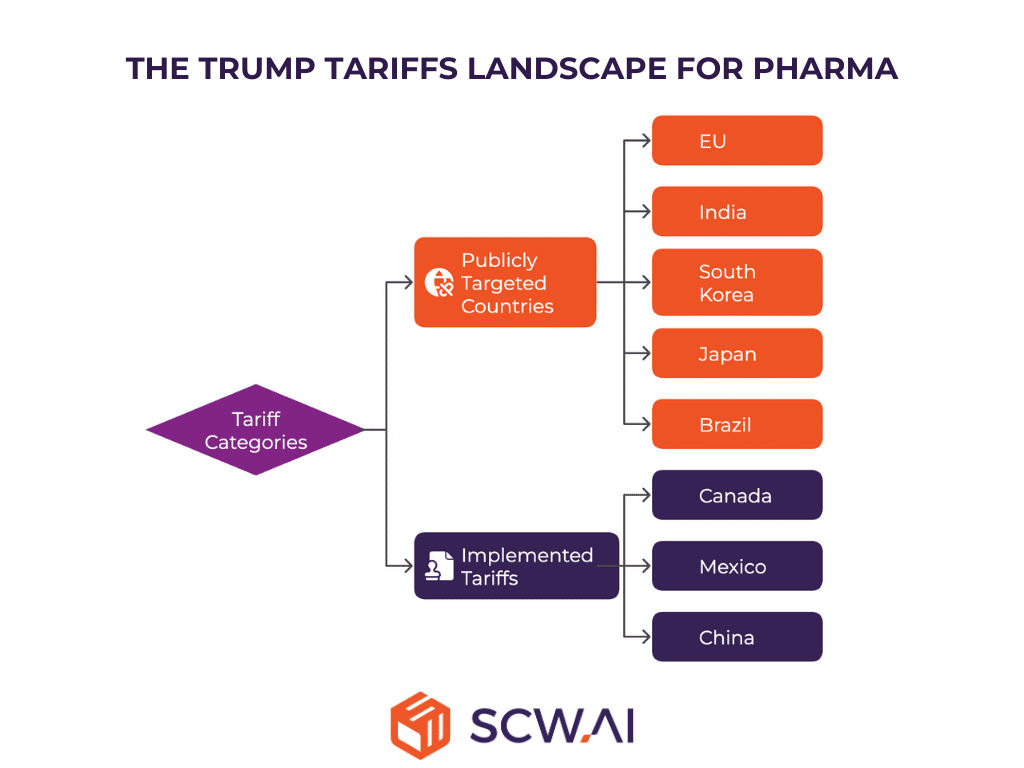
Several countries and regions have been publicly targeted, creating a climate of potential trade conflict. The European Union, in particular, has faced heightened scrutiny, especially in light of retaliatory tariffs imposed by the EU in response to U.S. tariffs on aluminum and metal products. While pharmaceutical products have so far been excluded from these retaliatory measures, the situation remains fluid. According to the Wall Street Journal, as a response to the EU’s retaliation, a new round of retaliatory tariffs including EU pharmaceutical products with a 25% tariff rate is scheduled to be announced as of April 2nd.
It is also essential to recognize the impact of tariffs already in place. Imports from Canada, Mexico, and China, for example, are currently subject to tariffs. These existing tariffs are already affecting trade flows and have implications for the cost and availability of pharmaceutical products.
A Snapshot of U.S. Pharmaceutical Trade: Setting the Stage
To accurately assess the potential consequences of Trump Tariffs, a thorough examination of U.S. pharmaceutical trade is essential. This analysis, drawing on data from the CEPII-BACI database (which utilizes UN Statistical Division data), provides a comprehensive overview of global trade patterns and reveals crucial insights into the dynamics of the U.S. pharma market.
Key Trade Data Insights
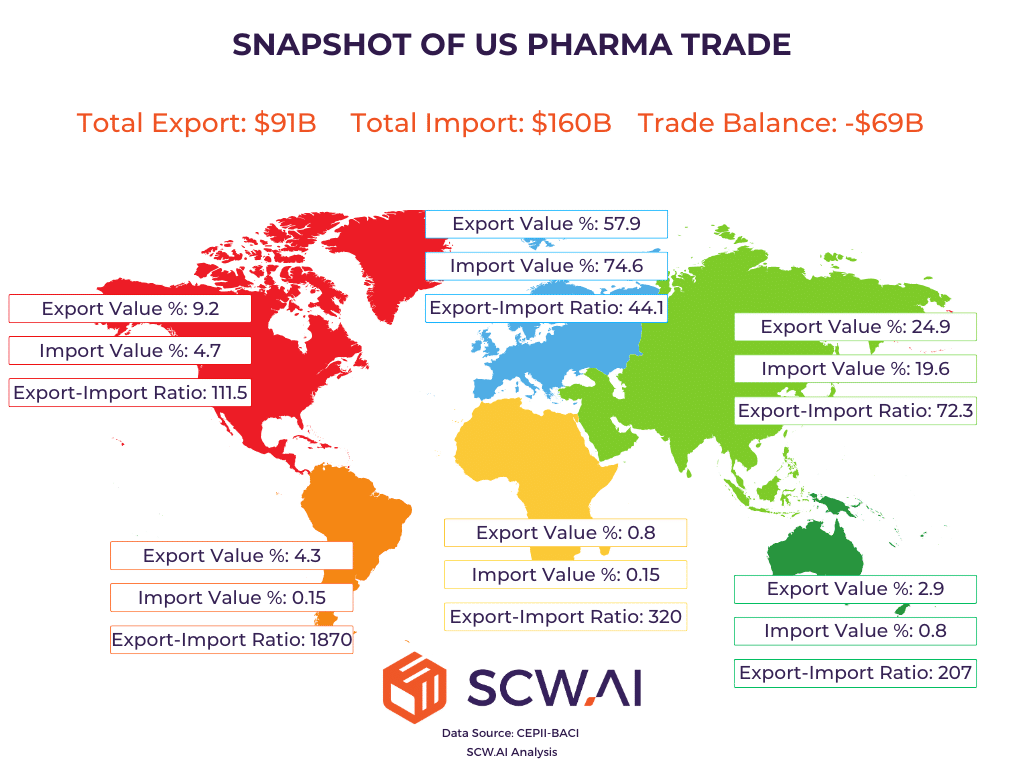
The data reveals a complex picture of U.S. pharmaceutical trade in 2023:
- Trade Deficit: The U.S. exhibits a pharmaceutical trade deficit of approximately $70 billion. With annual pharmaceutical exports around $91 billion and imports reaching approximately $160 billion, this substantial deficit raises concerns about trade imbalances and the potential for further tariff action.
- Export Destinations: A significant portion of U.S. pharmaceutical exports is directed towards Europe.
- Import Origins: A substantial portion of U.S. pharmaceutical imports originates from Europe.
- Trade Volume: North America and Asia are key trade partners for the U.S. in terms of the weight of pharmaceutical goods exchanged.
- Product Value: U.S. pharmaceutical companies tend to export high-value, low-volume products, while importing lower-value, high-volume products. If we index Value-to-Weight export value 100, for import, the index becomes 77.27.

A Critical Trade Imbalance: Unveiling Vulnerabilities
A deeper analysis of U.S. pharmaceutical trade data reveals a critical trade imbalance with the potential to trigger significant drug shortages and simultaneously create reshoring opportunities. To uncover this imbalance, we analyzed Combined Nomenclature (CN) codes, the international classification system that categorizes traded goods, including 45 specific pharmaceutical product categories.
Our analysis revealed a striking disparity: just 6 of the 45 pharmaceutical product categories account for a staggering $72 billion U.S. trade deficit. In stark contrast, the remaining 39 categories show a combined U.S. trade surplus of $2 billion. This dramatic difference underscores the potential for tariffs to severely disrupt the availability of certain essential medicines, particularly if domestic production cannot rapidly compensate for reduced imports.

If you want to identify the six CN codes responsible for a $72 billion deficit—crucial insights for strategizing your capacity increase in the U.S.—and explore a country-level breakdown of both U.S. pharma imports and exports, download our free eBook.
The Economic Impact: Opportunities and Challenges for Pharma
Trump Tariffs are not a monolithic force; they present a complex mix of both opportunities and challenges for the pharmaceutical industry. Understanding these multifaceted impacts is crucial for strategic planning.
Short-Term Impacts: Navigating Immediate Disruptions
The short-term effects of Trump Tariffs are likely to be felt within the first year of implementation. These include:
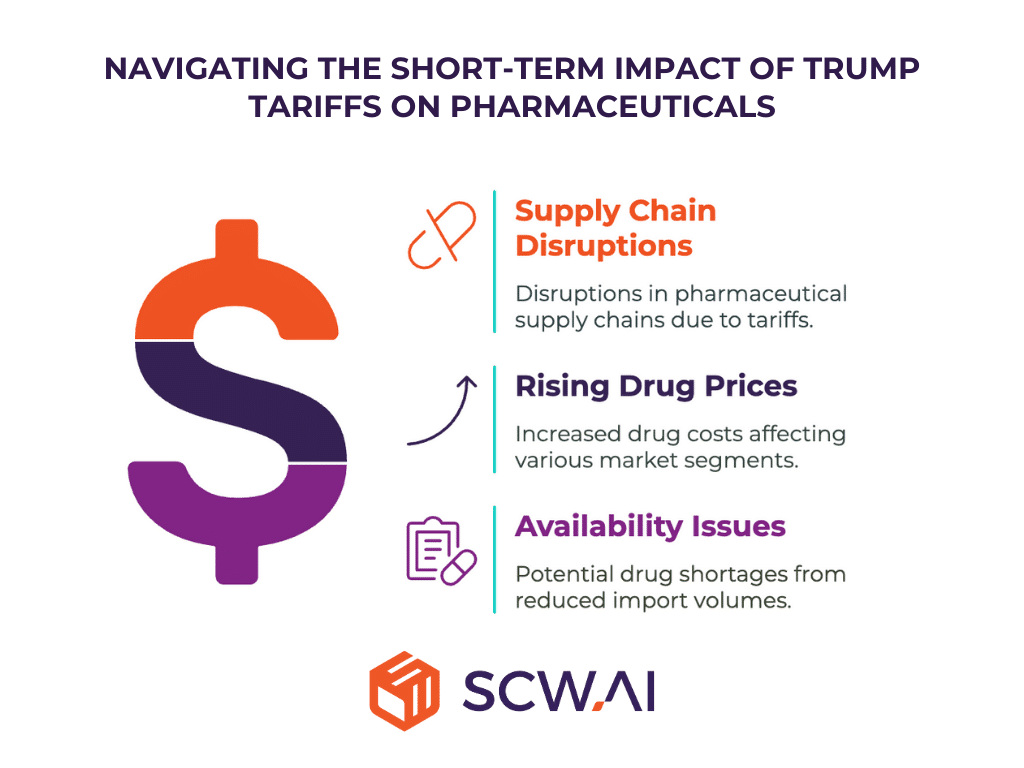
Supply Chain Disruptions
The imposition of tariffs can immediately disrupt established pharmaceutical supply chains. Companies that rely heavily on imported raw materials, intermediates, and finished products will face logistical challenges, potential delays, and reduced import volumes due to increased costs. This disruption can affect production schedules, increase lead times, and create uncertainty in the market.
Rising Drug Prices
Increased costs resulting from tariffs are likely to translate into higher drug prices for consumers. The impact will vary across different market segments. Low-profit-margin goods, such as generic drugs, are likely to see the cost burden fall primarily on consumers, as manufacturers have limited pricing flexibility.
High-profit-margin goods, such as branded medicines, may see cost increases shared between producers and consumers. Even domestically produced drugs may experience price increases due to higher costs for imported intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
Drug Availability Issues
Tariffs can reduce import volumes, potentially leading to drug shortages, particularly for essential medicines.
Long-Term Transformations: Reshaping the Industry
The long-term effects of Trump Tariffs are likely to unfold over a period of one to five years. These include:
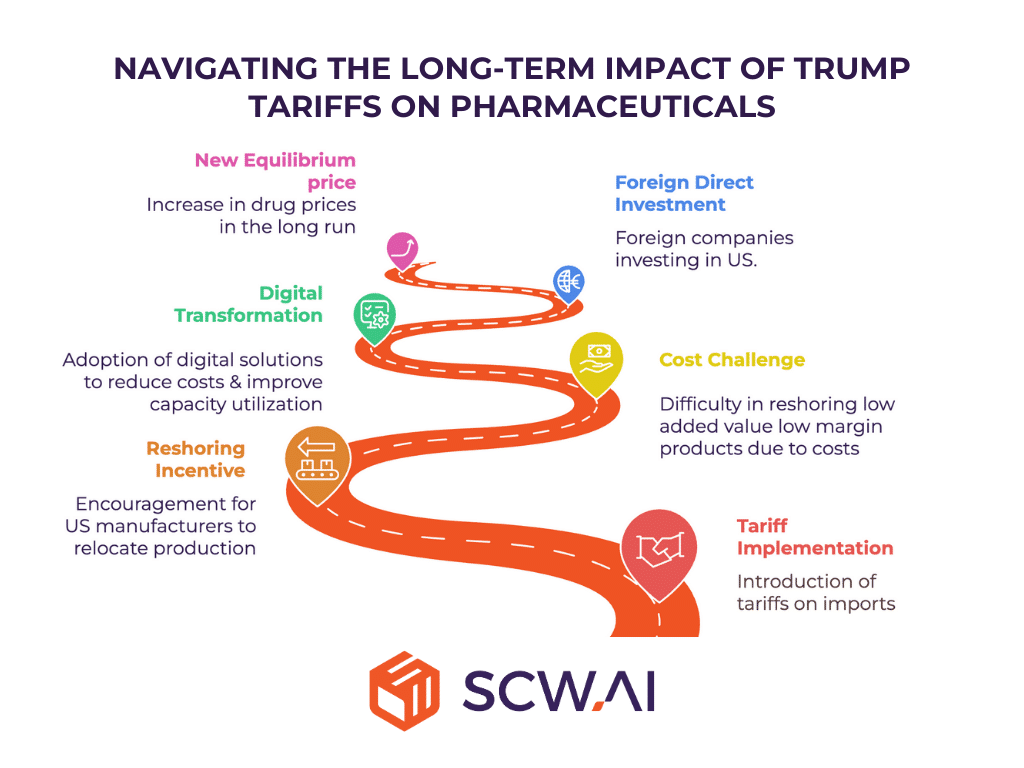
Reshoring U.S. Pharma Manufacturing
Tariffs can provide a significant incentive for reshoring pharmaceutical manufacturing to the United States. For example, if a U.S. manufacturer’s production costs are 20% higher than those of a foreign competitor, the 25% tariff can make domestic production economically feasible. This can lead to investments in new factories, production lines, and capacity expansion.
Attracting Foreign Direct Investment
The prospect of tariffs may encourage foreign pharmaceutical exporters to establish manufacturing facilities in the U.S. or engage in mergers and acquisitions with U.S. companies to circumvent tariffs, particularly if the U.S. market is crucial to their business.
Trump tariffs can also reduce foreign direct investment (FDI) outflow from the U.S., as the returns on investments in overseas manufacturing decrease. For instance, Pfizer’s CEO, Albert Bourla, has indicated that the company could shift overseas production to the U.S. if tariffs become a significant factor. Similarly, Eli Lilly has announced $27 billion investments in expanding its U.S. manufacturing capacity.
The New Price Landscape
Following the implementation of tariffs, drug prices are likely to undergo a period of adjustment. Initially, prices will likely spike as the immediate impact of tariffs is felt. Over time, prices are expected to reach a new equilibrium, higher than pre-tariff levels but lower than the initial spike, as domestic production increases and the effects of competition and the experience curve are realized.
Overcoming Reshoring Roadblocks: Navigating Challenges
Reshoring pharmaceutical manufacturing in the U.S., while offering potential benefits, faces significant obstacles that must be addressed:
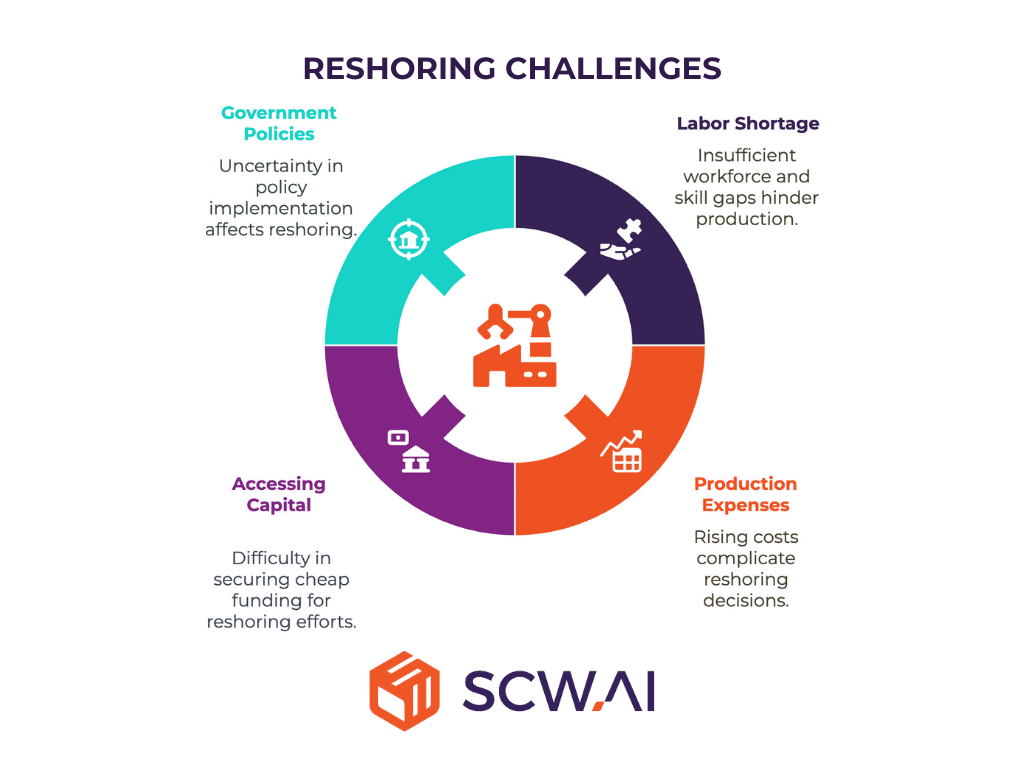
Labor Shortage and Skill Gaps
The U.S. manufacturing sector already grapples with labor shortages, and policies that restrict immigration can further exacerbate this issue. An aging workforce and a lack of interest in manufacturing careers among younger generations contribute to this challenge.
Managing Production Expenses
Manufacturing costs in the Far East and Mexico are often lower, sometimes way below 25% than in the U.S., primarily due to labor, energy, and regulatory expenses. U.S. manufacturers must find ways to reduce costs to remain competitive and mitigate price increases for consumers.
Accessing Capital
Expanding domestic pharmaceutical production requires substantial capital investment. However, current economic conditions, including interest rate fluctuations and stock market volatility, can make it challenging for companies to secure the necessary funding.
Policy Inconsistencies
Contradictions within government policies can create uncertainty and hinder reshoring efforts. For example, policies that promote domestic manufacturing while simultaneously restricting immigration can create a labor bottleneck.
The Power of Digital Transformation: A Strategic Imperative
Digital transformation offers a powerful strategic response to many of the challenges and opportunities presented by Trump Tariffs. It enables pharmaceutical manufacturers to:
- Maximize Capacity Utilization: Digital tools and technologies can optimize production processes, reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and increase throughput.
- Reduce Costs: Automation, artificial intelligence (AI), manufacturing analytics, and other digital solutions can help manufacturers streamline operations, minimize expenses, and enhance profitability.

Digital Transformation in Action: Key Applications

- End-to-End Factory Visibility: Digital solutions provide real-time data and insights, enabling manufacturers to optimize root cause analysis, identify bottlenecks, and implement proactive maintenance strategies.
- Labor Analytics: Analyzing labor data can improve workforce efficiency, identify skill gaps, and personalize training programs.
- AI-Driven Automation: Artificial intelligence can automate complex tasks, optimize production schedules, predict equipment breakdowns, and enhance quality control processes.
- Digital Quality Documentation: Digital documentation systems such as Digital Logbooks can streamline quality processes, reduce errors, improve compliance, and free up staff time for more productive activities.
Quantifying ROI of Digital Factory Transformation for Pharma
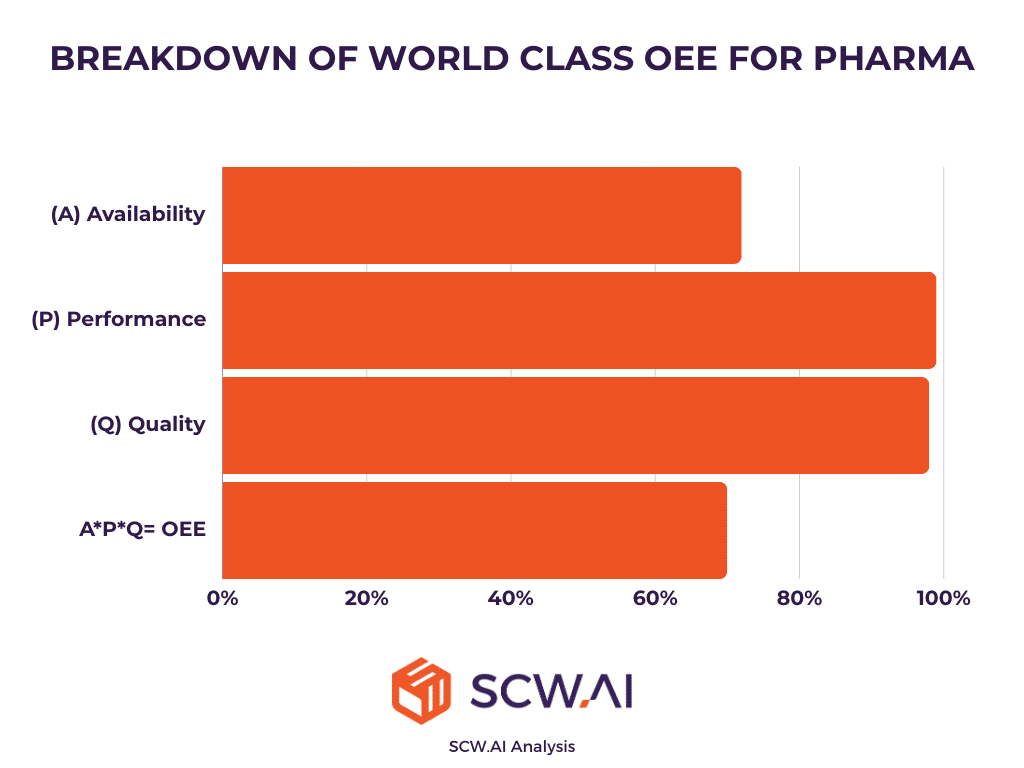
OEE gains thanks to digital transformation can be utilized as a proxy for estimating cost reduction and throughput increase. According to our analysis, the average pharmaceutical factory operates at an OEE of 37%. In contrast, top 10% quartile factories that implement end-to-end digital transformation, achieve OEE metrics of 70%, representing a 33 percentage point increase. This improvement can nearly double production output or halve the time required to meet annual production goals, depending on the allocation of productivity gains.

To quantify the potential ROI of increasing OEE from 37% to 70%, we employed our Advanced ROI Calculator, which estimates business returns based on user-defined input variables. For this scenario, we assumed a pharmaceutical factory operating 16 hours per day, 250 days per year, with 20 production lines and 5 workers per line. We also assumed an hourly operator cost of $30, annual revenue of $18 million, and a gross margin of 15%.
The initial OEE was set at 37%, with 47% availability, 82% performance, and 96% quality. Post-digital transformation, we assumed an OEE of 70%, with 72% availability, 99% performance, and 99% quality. To reflect U.S. manufacturers’ priorities of increasing throughput while reducing costs, we allocated 75% of OEE gains to production increases and 25% to cost savings.
This scenario yielded the following projected returns:
- 68% increase in throughput
- $1.83 million in additional profit
- $2.79 million in cost savings from direct labor, maintenance, depreciation, and materials
- Total projected annual return of $4.63 million

Choosing the Right Technology Partner: Essential Criteria
To successfully implement digital transformation and navigate the challenges of the new trade landscape, it is crucial to partner with the right technology vendor. Key considerations include:
- Scalable Solutions
- End-to-End Solutions
- Pharmaceutical Expertise
- Regular Software Updates and Future-Proofing
- Speed and Ease of Deployment
- Strong Customer Support
- Compliance and Certifications
- GMP Compliance for Paperless Solutions
Download Free eBook to Navigate Trump Tariffs for Pharma

For a more in-depth analysis, practical guidance, and actionable strategies, we encourage you to download our free eBook: This comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and tools you need to minimize risks and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Modernize Your Factory with SCW.AI
SCW.AI offers an end-to-end Digital Factory Platform designed to optimize your operations in this new trade environment. Our solutions address key challenges, from maximizing capacity utilization and reducing costs to ensuring GMP compliance and agile scheduling. By partnering with SCW.AI, you can build a resilient, future-proof pharmaceutical factory, capable of navigating the uncertainties of Trump Tariffs and emerging stronger than ever.
Do not let tariffs dictate your future. Book a demo today to explore how SCW.AI can empower your pharmaceutical manufacturing to thrive in the face of these changing trade policies.
If you have further questions regarding Trump Tariffs and their impact on the pharma industry or our solutions you can contact us.
Get Your Free "Trump Tariffs Pharma eBook"
Fill out the form to request your free download.