In the realm of industrial automation, the Modbus protocol has emerged as a cornerstone technology for seamless communication between Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and various devices within a factory setup. This article delves into the intricacies of Modbus PLC, exploring its communication methods, comparison with other methods of collecting data like OPC, its advantages, drawbacks, and practical applications in modern manufacturing environments.
What is Modbus Communication in PLC
Modbus Communication in PLC represents a pivotal method for gathering data within industrial environments, minimizing the need for manual data collection and entry. It forms the backbone of automated data acquisition systems, seamlessly connecting Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) with a myriad of devices including sensors, actuators, and Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs).
The essence of Modbus lies in its ability to provide high-quality data streams, facilitating the generation of automated dashboards, AI models, and digital twins that enhance the operational efficiency of manufacturers. By leveraging Modbus, factories can tap into a wealth of real-time information, enabling informed decision-making and proactive maintenance strategies.
The World of Bits
At its core, the data collected via Modbus PLC connections manifests as a series of bits, comprising a binary language of zeros and ones. While inherently valuable for machines and automated systems, this raw data holds limited meaning for most individuals, unless they possess expertise in hexadecimal language derived from bits (See Figure Below).
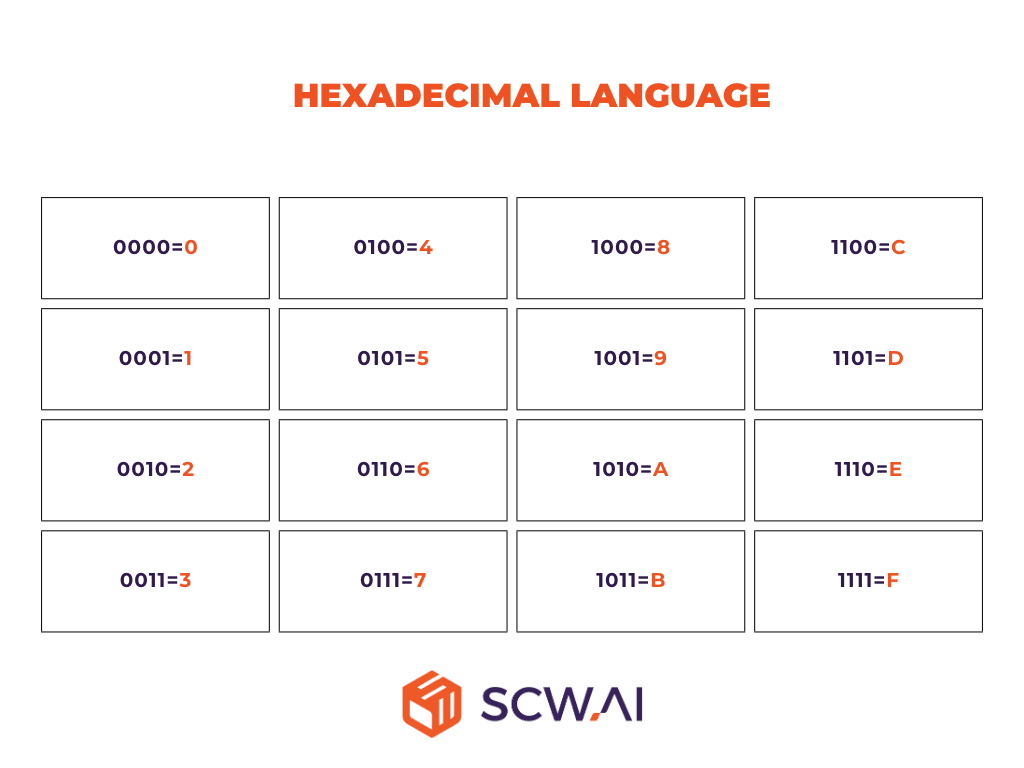
Enterprises often rely on Internet of Things (IoT) devices to bridge this gap, converting Modbus PLC data into a human-readable format. These IoT solutions serve as interpreters, translating the cryptic language of bits into intuitive visualizations and actionable insights accessible to executives and decision-makers. This transformation empowers organizations to unlock the full potential of shop floor data.
3 Types of Modbus PLC Connection
1. Serial Modbus (RTU)
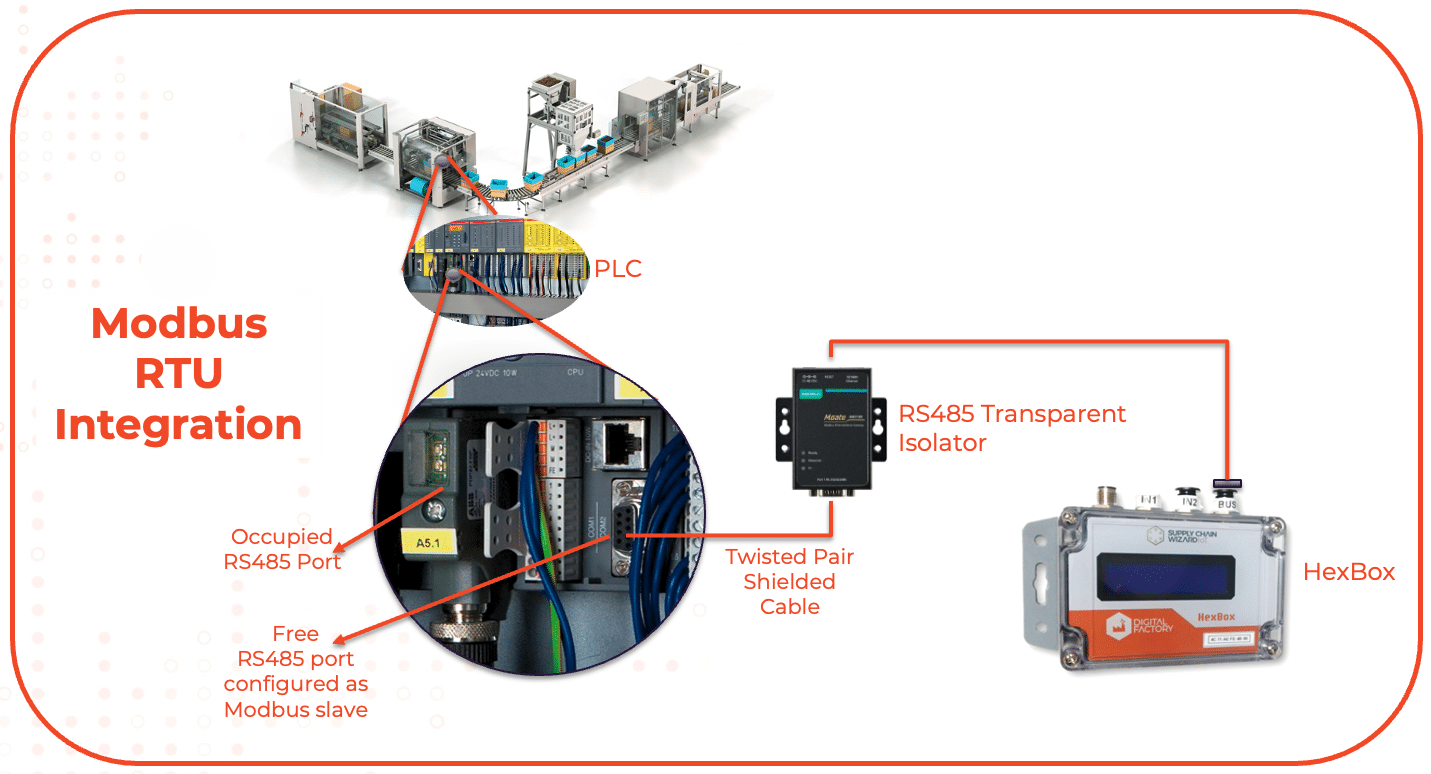
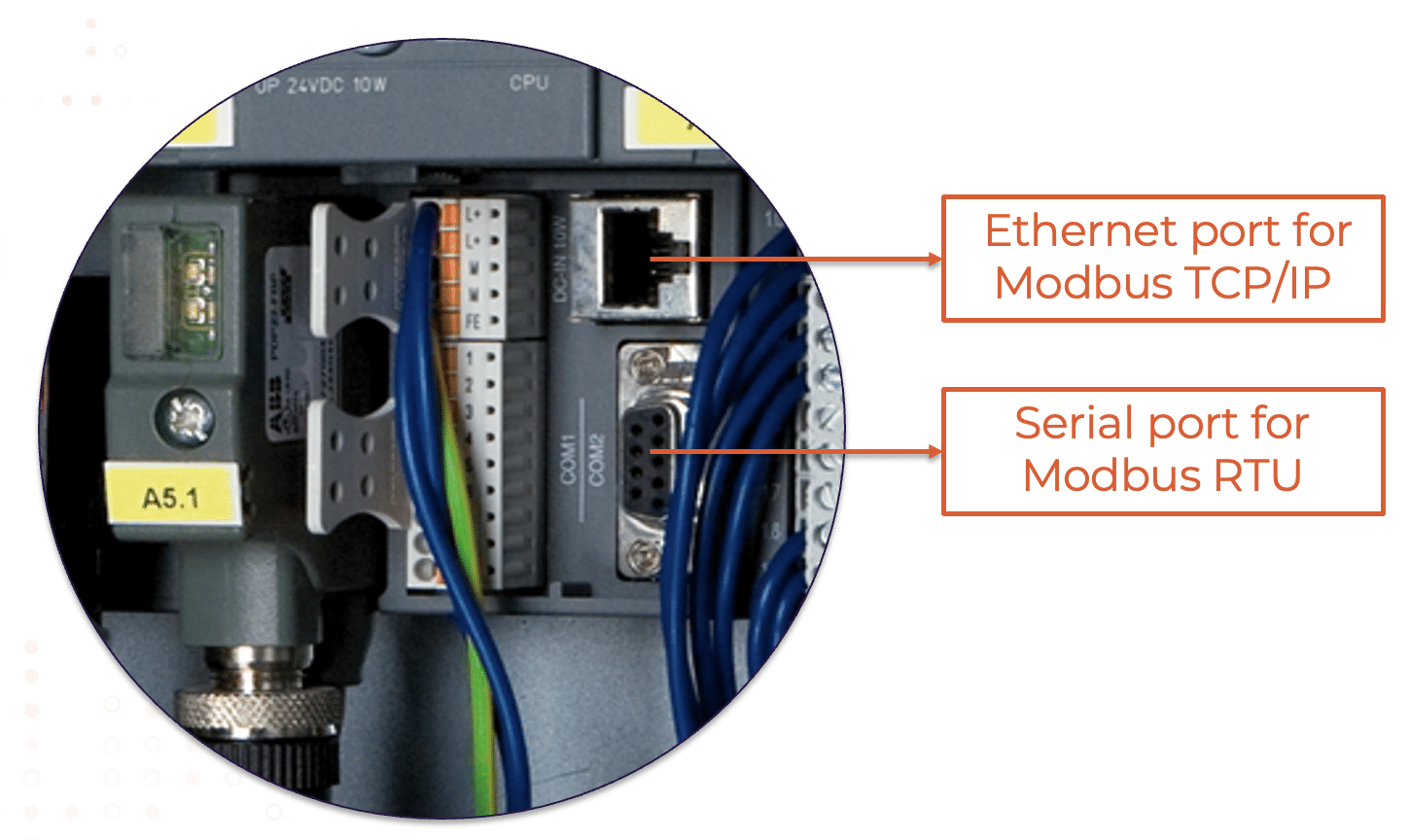
Serial Modbus, particularly in its Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) configuration, stands as a foundational pillar in industrial communication protocols, akin to the HDMI ports found on the backs of televisions or the ubiquitous USB ports on computers. These connection points, be they RS485, RS232, or similar, serve as the conduits through which Modbus RTU establishes communication between PLCs and peripheral devices.
Ideal for small to medium-sized factories with a limited number of production lines, the RTU connection offers simplicity and cost-effectiveness. However, its practicality diminishes in the face of complex industrial setups characterized by numerous interconnected systems.
While RTU may lack the bandwidth to efficiently handle the data demands of larger factories with dozens of production lines, it remains a highly reliable and cost-effective solution for smaller-scale operations. Its prevalence as the most primitive yet effective method for automated data gathering underscores its enduring relevance in industrial automation.
2. Ethernet Modbus (TCP/IP)
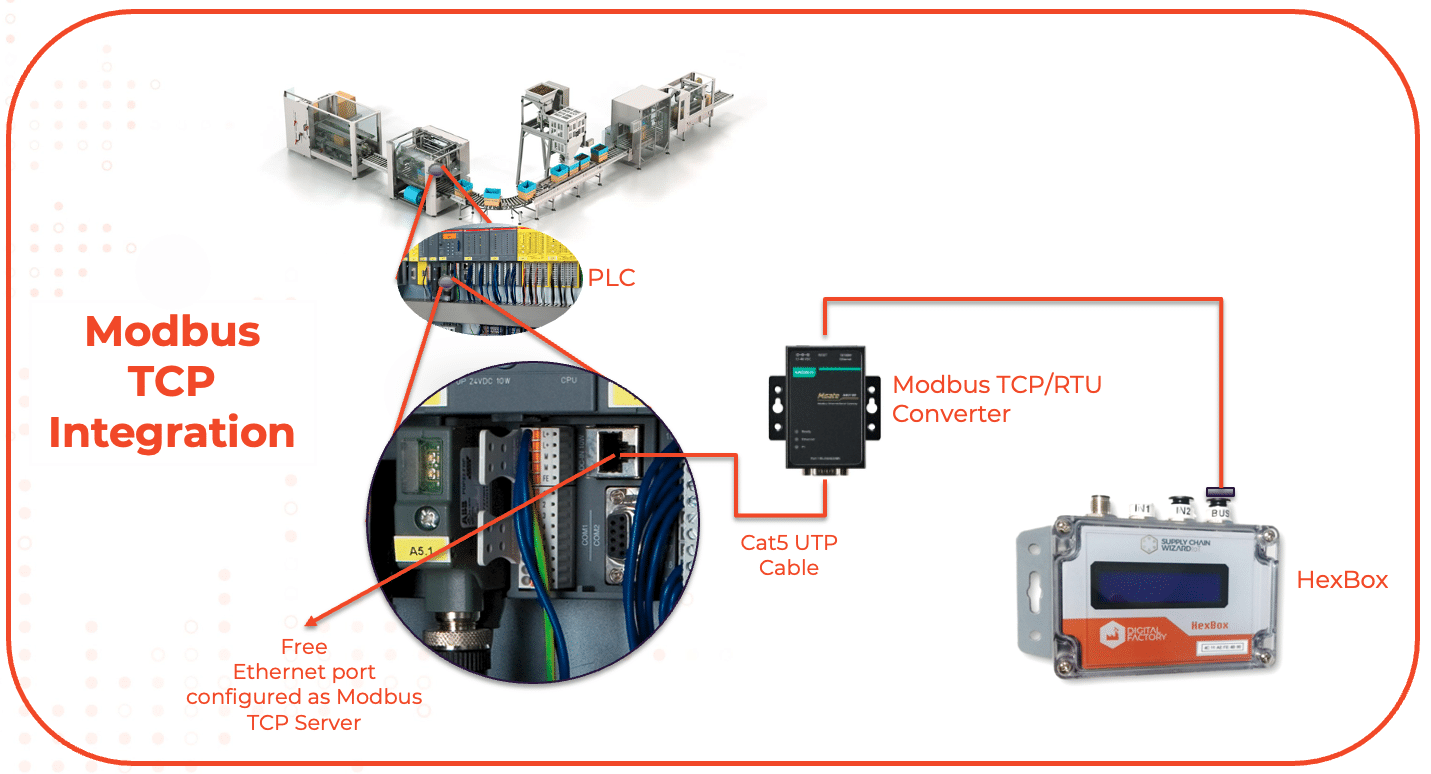
Ethernet Modbus, which leverages the TCP/IP protocol, provides connectivity in industrial automation, similar to integrating internet access within the shop floor environment.
One of the main features of Ethernet Modbus is its ability to connect machines on Local Area Networks (LANs), enabling seamless communication with every device connected to the network. This broader reach and scalability make Ethernet Modbus well-suited for larger factories with extensive production lines and a multitude of interconnected systems.
As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, Ethernet Modbus emerges as one of the de facto standards for efficient and comprehensive data communication in factory automation.
3. Modbus ASCII
Modbus ASCII employs ASCII encoding for data transmission, making it human-readable and suitable for troubleshooting and diagnostic purposes. However, despite these benefits, it is rarely harnessed by factories for automating data gathering as of today.
Modbus PLC vs OPC for Effective Factory Data Collection and Interpretation
While both Modbus and OPC (open platform communications) serve as communication standards in industrial automation, they differ in their scope and functionality. Modbus primarily focuses on data exchange between PLCs and field devices, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness. On the other hand, OPC provides a standardized interface for accessing data from diverse industrial systems, enabling seamless integration with various software applications.
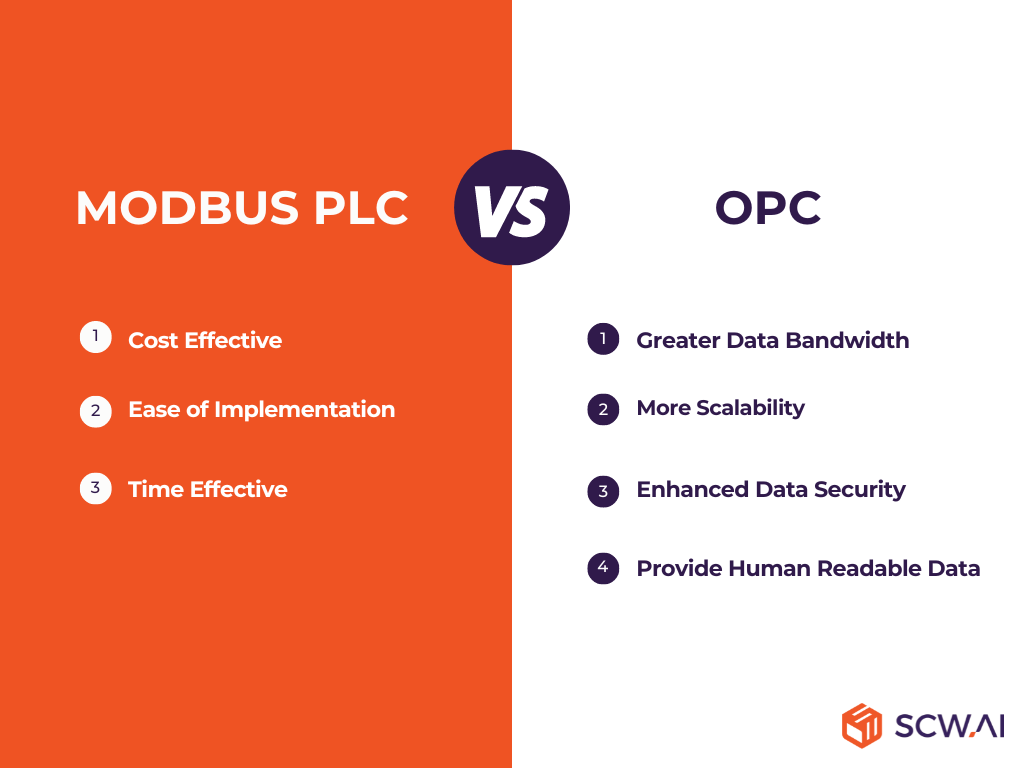
Pros of Modbus PLC
- Cost Effective: Modbus implementation typically incurs lower expenses compared to proprietary protocols, making it an attractive choice for budget-conscious projects.
- Ease of Implementation: With its straightforward communication structure and widespread support in PLCs and industrial devices, Modbus integration is relatively simple and code-free.
- Time Effective: Rapid deployment and configuration processes contribute to shorter setup times, accelerating project timelines and time to value.
Cons of Modbus PLC
- Limited Data Bandwidth: Modbus’s inherent limitations in data bandwidth may pose challenges in transmitting large volumes of data or high-frequency updates which can end up with failure for large AI deployments.
- Scalability: As the size and complexity of automation systems grow and the number of lines within the project increases, Modbus PLC connections may encounter scalability issues, necessitating alternative solutions or protocol upgrades.
- Data Security: The lack of built-in security features in Modbus protocols raises concerns regarding data integrity and vulnerability to cyber threats. To reduce the risk of data losses and leakages, factories might need to invest in technologies like firewalls, software defined perimeters, ZTNA systems and more.
- Need for Software That Makes Data Human Readable: While Modbus data is machine-readable, converting it into a human-readable format often requires additional software tools or custom solutions which end up with additional integration of IoT tools frequently.
Which Solution Should Factories Prefer?
It is important to note that these pros and cons may vary depending on the type of Modbus PLC used. For example, Ethernet Modbus is more scalable compared to Serial Modbus, while Modbus ASCII provides more human-readable data. However, the generalization above holds true when comparing OPC connection with Modbus PLC for data collection in factories.
In this regard, we can say that Modbus PLC connection might be suitable for small and medium-sized factories, where the number of lines and project complexities are typically manageable with this technology, and where factories can benefit from cost-effectiveness.
On the other hand, for large factories with over a hundred lines and generally having initiatives for more complex AI/digital twin models, SCW.AI recommends harnessing OPC as an alternative.
How Factories Can Utilize Modbus PLC Data in Shop Floor
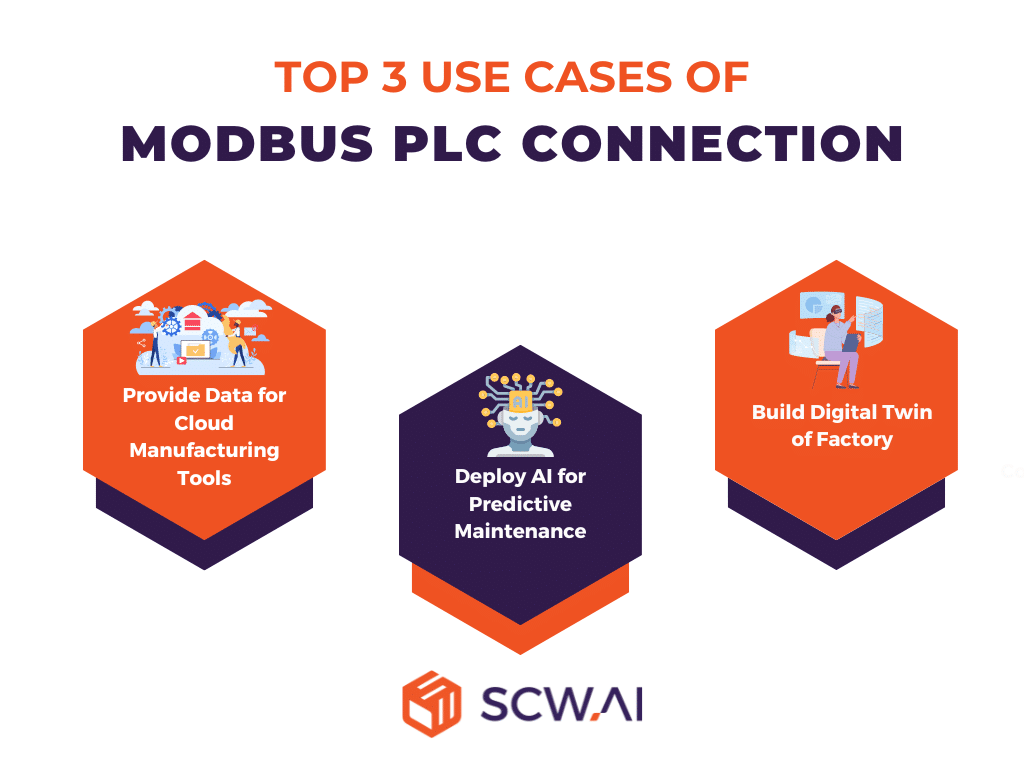
Provide Data for Cloud Manufacturing Tools
Integrating Modbus PLC data with cloud-based manufacturing platforms enables real-time monitoring, analytics, and remote management of factory operations.
In this way, factories can improve their KPIs such as OEE (See image below), takt time, OTIF score and many more.

Deploy AI for Predictive Maintenance
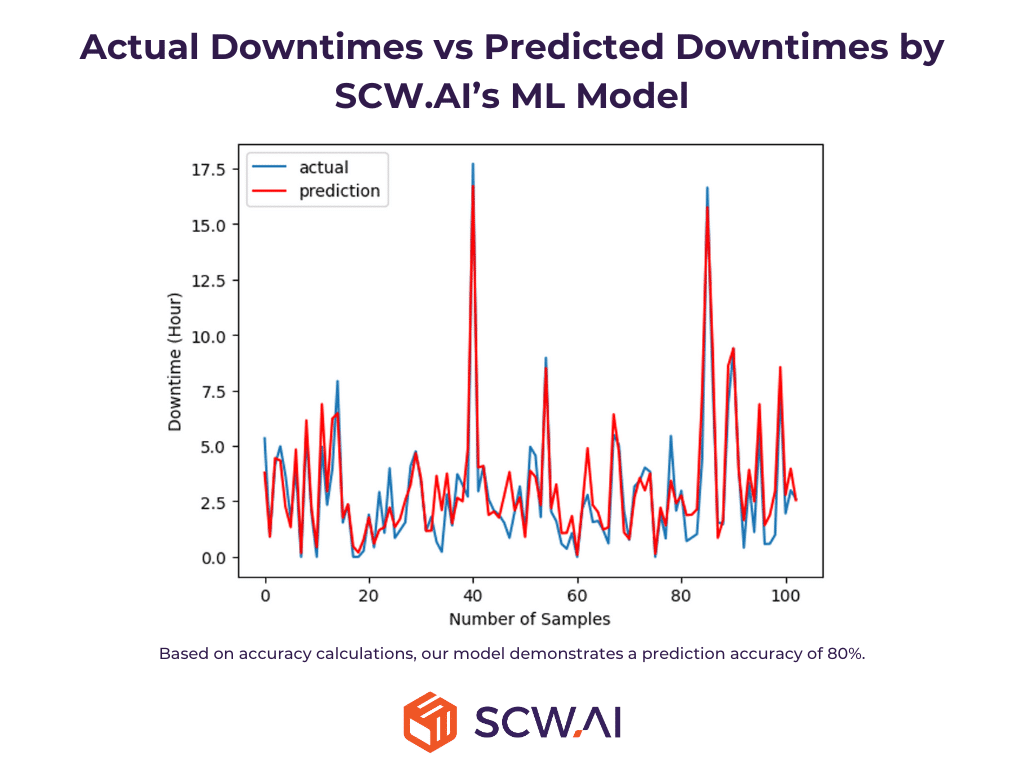
AI models are as effective as the data they are trained on. Therefore, for manufacturers that want to harness AI for increasing efficiency Modbus plc connections might be handy.
By analyzing historical data collected through Modbus PLC, AI algorithms can predict equipment failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and prevent costly downtime around 15% per Deloitte.
Build Digital Twin of a Factory
Utilizing Modbus data, manufacturers can create digital replicas of their production facilities, facilitating simulation, optimization, and virtual testing for process improvement and innovation.
The following conversation between Evren Ozkaya, Ph.D., CEO and Founder of SCW.AI, and Mike Walker, Executive Director of Global Healthcare and Life Sciences Digital Strategy at Microsoft, from the fifth episode of the Supply Chain Wizard for Pharma podcast series, illustrates how data is the cornerstone for deploying any cutting-edge technology on the shop floors. From this perspective, we can add utilization of any digital lean technology as Modbus PLC application.
How can SCW.AI Assist Factories for Data Collection and Digitalization
SCW.AI emerges as a transformative ally for factories seeking to harness the power of data through automated collection and digitalization. By seamlessly integrating Modbus PLC and OPC connections from machines to the Digital Factory Platform—a SaaS tool developed by SCW.AI for manufacturers—companies unlock a wealth of possibilities for data-driven decision-making and process optimization.
For factories opting for Modbus PLC connections or facing infrastructure constraints unsuitable for OPC integration, SCW.AI offers innovative IoT tools designed to bridge the gap between machine-readable bits and human-readable data. Through this conversion process, raw data becomes readily interpretable, empowering both machine diagnostics and strategic decision-making.
Once high-quality data is securely collected, SCW.AI provides a suite of solutions to maximize its utilization:
- Real-Time Dashboards and Reports: SCW.AI delivers over 50 reports and dashboards, furnishing crucial insights such as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), maintenance metrics like Mean Time to Failure (MTTF), augmented takt time, Total Effective Equipment Performance (TEEP), and more. These intuitive visualizations enable informed decision-making and proactive maintenance strategies in real-time.
- Custom Reports: Recognizing that each factory possesses unique operational priorities and KPIs, SCW.AI offers tailored solutions to generate custom reports. By focusing on specific metrics critical to your operations, these personalized insights empower you to monitor and optimize performance with precision.
- AI Algorithms: Leveraging the power of AI, SCW.AI develops both generic and custom algorithms tailored to your factory’s needs. From AI schedulers optimizing production schedules to predictive maintenance algorithms preemptively identifying equipment failures, these AI-driven solutions automate decision-making processes, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
To embark on your journey towards digital transformation and discover the full potential of the Digital Factory Platform and SCW.AI, book a demo today.