As a manufacturer, have you considered the financial gains you might be missing out on by not optimizing your scheduling through the implementation of advanced planning and scheduling systems? Scheduling problems in manufacturing are often categorized as NP-hard (Nondeterministic Polynomial Time), and in some instances, NP-complete problems. This classification indicates that finding an optimal solution, if it exists, is practically impossible with current computing power. In fact, solving NP problems is such a formidable challenge that the Clay Mathematics Institute offers a $1 million reward for significant contributions to computer science and mathematics in this area.
While achieving perfect scheduling may be an impossible endeavor, striving for near-optimal solutions and maximizing profits through advanced planning and scheduling systems is feasible. An illustration of this potential comes from one of our clients who asked us to develop new scheduling algorithms for a limited subset of six production lines as a demonstration. Upon comparing the results with their existing scheduling, using the same cost function, they discovered that the improved scheduling for just six lines led to a monthly cost reduction of $100,000.
For large manufacturers operating 24/7 with numerous production lines, the potential financial gain of improving scheduling can extend into the millions of dollars. This article provides insights into how companies can enhance their scheduling processes with new technologies. Initially, we will define advanced planning and scheduling in the era of Industry 4.0, then we will outline the challenges in finding near-optimal solutions for scheduling. Subsequently, we will explore the advantages and practical applications of AI and ML models in determining schedules. In the end, we will illustrate how advanced scheduling systems can address diverse optimization needs based on specific business requirements.
What is Advanced Planning and Scheduling
Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) is the augmentation and automation of manufacturers’ scheduling activities through digital tools that enhance agility and visibility. Empowering scheduling executives with real-time information on key metrics such as schedule adherence, compliance, and attainment enables them to make informed and timely decisions. This data-driven approach enhances the precision of decision-making, ensuring that executives can proactively manage schedules, optimize resource allocation, and drive operational efficiency.
In addition, by leveraging advanced analytics, machine learning algorithms, and heuristics, APS systems assist manufacturers in generating automated optimal-like schedules tailored to unique business requirements, such as:
- Makespan minimization
- OTIF maximization
- Cost minimization and more. This results in increased profitability and capacity utilization for manufacturers.
APS systems can seamlessly integrate with existing supply chain digital infrastructure, including Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). Alternatively, APS software can be implemented as a standalone tool to orchestrate workflows within the shop floor.
What are the Major Components of Advanced Planning and Scheduling Systems?
Advanced planning and scheduling systems have three main components namely:
- Demand Planning: Involves estimating the quantity of products a manufacturer should produce over a specified period, typically broken down into shorter intervals like years and months.
- Production Planning: Is the strategic positioning of a manufacturer over the long term in anticipation of expected demand. This planning process often considers longer time intervals compared to scheduling.
- Production Scheduling: Is the detailed execution plan for a shorter time interval, often a week or a month, designed to fulfill the objectives outlined in the production planning phase.
Why Do Manufacturers Need APS Systems?
Manufacturers need advanced planning and scheduling software to effectively solve complicated scheduling activities. Scheduling is the intricate process of orchestrating work sequences, managing time, and allocating resources to align with customer demand, work order due dates, and the quality expectations set by both customers and regulatory authorities.
A scheduling activity should adeptly address the followings:
- Resource Allocation: Schedulers meticulously determine the allocation of resources, deciding which production lines will be utilized, the quantity of specific raw materials to be used, and who will operate certain lines to produce a specific output.
- Time Management: Organize work orders considering their due date.
- Sequencing: Putting production tasks in the right order to guarantee a productive workflow, minimal downtime and idle time, and effective use of resources.
- Capacity Planning: Measuring the production capacity of a factory to avoid over/under production.
- Demand Prediction: Project demand to help the factory get ready for anticipated future work orders.
- Optimization: Create algorithms to carry out more efficient work order scheduling in order to cut expenses, improve work order delivery time, and maximize profit.
As the number of lines, work orders, customers to manage, workforce, and interdependencies among tasks (e.g., coating preceding packaging as illustrated in the figure below) grow, the challenge of determining the optimal scheduling solution becomes increasingly intricate since the number of possible schedules increases exponentially. Additionally, conflicting objectives for scheduling arise; for instance, cost minimization may conflict with delivering work orders on time. Finally, the dynamic nature of the shop floor, coupled with fluctuations in customer demands, further challenges the quest for optimal scheduling.
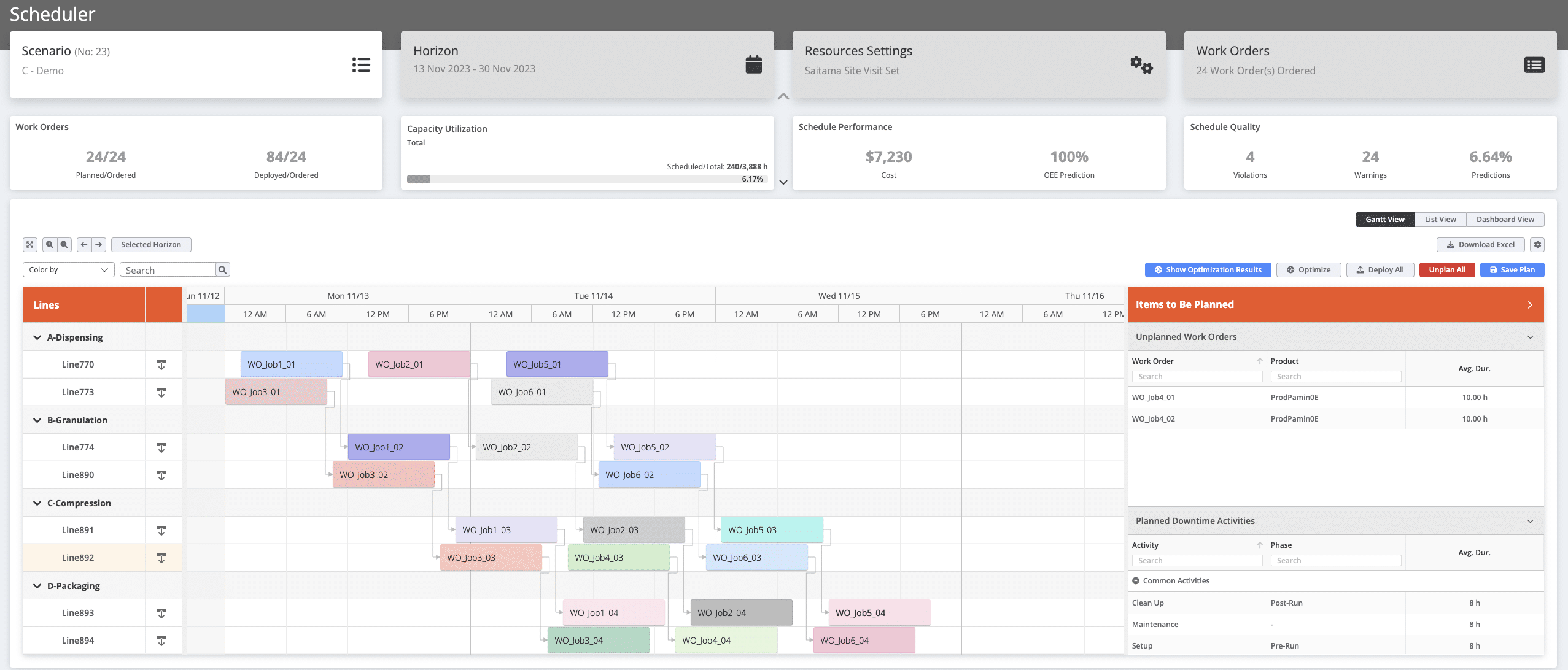
The Role of AI in APS
In the manufacturing context, AI serves as an automation technology for complex and repetitive tasks. The exceptional computational power of AI/ML models enables them to outperform humans in tasks for which they are specialized, and scheduling is one of the prime examples. In this context, AI/ML models form the core of well-functioning advanced planning and scheduling software.

The benefits of utilizing AI for scheduling activities can be illustrated in 3 main points:
1. Reduce Labor Hours for Scheduling by Half
Boston Consulting Group (BCG) reports that implementing AI for scheduling automates computational tasks and cuts scheduling-related activities of workers by 50%. This enables employees to allocate their time to other essential activities.
Below video illustrates how SCW.AI’s APS software automates scheduling decision making once work order information is provided:
2. Enhance Productive Time by 30 Minutes Daily
According to BCG, AI-driven scheduling has been shown to enhance overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by just over 3%, resulting in an equivalent of 30 minutes of additional productive time for factories. The main driver of OEE improvement is coming from reduction in changeover duration.
On the flip side, AI models can deliver an additional enhancement in run time of up to 20%, as per Deloitte, by automating maintenance scheduling activities through predictive maintenance. This proactive strategy aids manufacturers in organizing maintenance schedules just before equipment breakdown by utilizing historical factory and machinery data. Consequently, further improvements in OEE become achievable by addressing unplanned downtime.

To discover the average and world-class OEE for pharmaceutical manufacturers, along with strategies to improve it, you can check out our article “World Class OEE in Pharma: A Benchmarking Analysis.”
3. Cost Reduction
As highlighted earlier, AI-driven scheduling can result in a direct cost reduction of >$100,000 per month when implemented for six production lines in a factory operating 16 hours on weekdays. For larger manufacturers, this translates into potential savings of millions of dollars. Furthermore, improved productive time due to AI scheduling enhances your On Time In Full (OTIF) score, reducing the likelihood of incurring OTIF penalties.
Top 5 Use Cases of APS Systems for Manufacturers
Through the integration of sophisticated analytics, heuristic algorithms, simulations, and mixed-integer programming, advanced planning and scheduling systems have the capability to automate and enhance five distinct scheduling tasks, as demonstrated below.
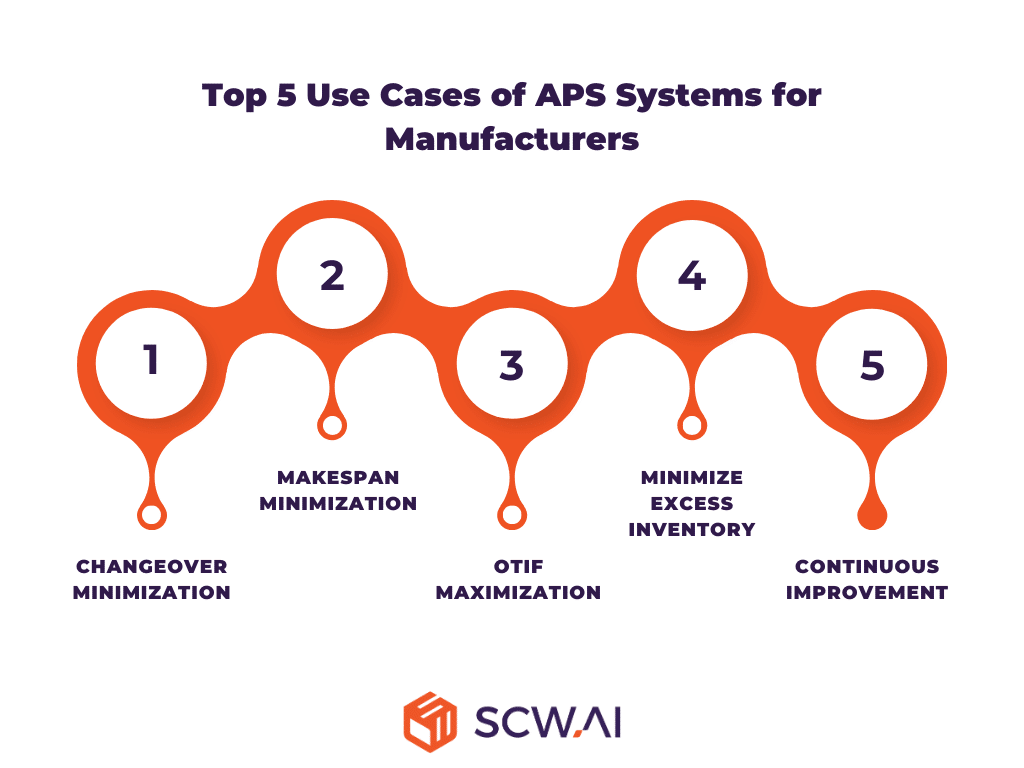
1. Changeover Minimization
APS Software optimizes the sequencing of work orders to minimize the number of major changeovers. This is achieved by strategically replacing major changeovers with more minor ones, ensuring that production quality is maintained and compliance with regulations is upheld. The key to this approach lies in sequencing products with similar raw materials, allowing cleaning staff to allocate less time for preparing lines for the next work order.
This application of APS systems can be specifically profitable for pharmaceutical manufacturers where regulations like cGMP force companies to dedicate a crucial time for line cleaning activities.
2. Makespan Minimization
Advanced algorithms of APS systems assign each work order to machines, aiming to minimize the overall time required for completion. This task is intricate due to the consideration of interdependencies among work orders. The challenge lies in strategic assignment and a comprehensive scheduling perspective, since a single work order assigned to the fastest-producing equipment, might inadvertently prolong the overall makespan and result in a sub-optimal schedule. This careful optimization contributes to streamlining production processes and reducing the time needed for the entire manufacturing cycle.
Such use cases can be beneficial for manufacturers that combat demand fluctuations. Makespan minimization allows them to address excess demand periods without delays in delivery since it reduces takt time.
3. OTIF Maximization
Advanced algorithms prioritize the production of work orders based on the proximities to due dates. This strategic approach enhances the OTIF score, resulting in greater customer satisfaction and a reduction in OTIF penalties, while ensuring that a buffer is taken into account to foresee potential hot work orders.
This use case is particularly advantageous for manufacturers bound by OTIF contracts, as APS software can assist manufacturers in avoiding penalties that could accumulate to a fortune.
4. Minimize Excess Inventory (Just in Time Delivery)
APS software, powered by AI algorithms and real-time monitoring, strategically organizes production schedules to minimize inventory and promote supplier collaboration. These systems ensure the precise delivery of finished goods when needed, enhancing supply chain visibility and adaptability. By preventing overproduction and minimizing the costs associated with maintaining unnecessary inventory, this approach optimizes resource utilization, reduces inventory holding costs and the risk of perishment and fosters a cost-effective manufacturing process.
Leveraging this application can be a game-changer for food and beverage industries, especially where the shelf life of products tends to be short.
To learn more about our JIT Scheduler read our article A Simplified Guide to Just in Time Scheduling for Manufacturers.
5. Continuous Improvement
As highlighted by McKinsey, a strategic approach to leverage an AI-scheduler involves integrating it with digital twins. Digital twins serve as valuable tools for training more effective algorithms through simulations. Deep learning models within digital replicas of factories can explore various resource allocation scenarios, refining the scheduler’s algorithms for improved performance.
Additionally, digital twins play a crucial role in master data optimization, a necessary component for high schedule adherence. For example, if there is a forecasted 25-minute changeover between two work orders according to your master data, but historical data from digital twins indicates a 40-minute duration, the APS system adjusts the scheduling using this empirical information. Thus, manufacturers can prepare more realistic schedules with greater schedule adherence scores.
How Can SCW.AI Improve Your Scheduling?

SCW.AI’s Digital Factory Platform empowers manufacturers to make agile decisions through a cloud based advanced planning and scheduling system. Utilizing AI algorithms and heuristics, companies can:
- Optimize changeover durations
- Minimize makespan
- Minimize cost
- Ensure just-in-time delivery
- Maximize OTIF performance, and more (see figure above).
The platform also offers comprehensive real-time insights into schedule adherence. Additionally, manufacturers can plan maintenance activities in a data-driven manner with the help of the Maintenance Performance Report. To explore further the value proposition of SCW.AI, you can book a demo now.