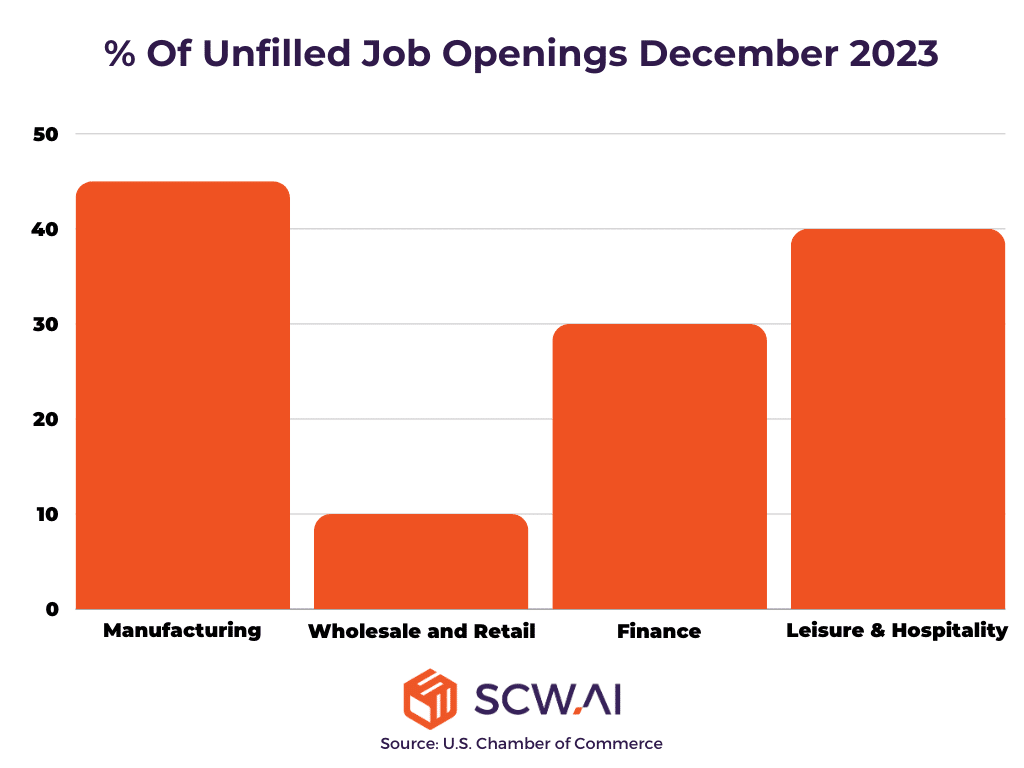
According to the US Chamber of Commerce, manufacturing is one of the industries most affected by the Great Resignation. As of the summer of 2023, over 615,000 job openings, equivalent to 45% of all job openings, remained unfilled. Labor shortage in manufacturing reduces the production capacity of factories and threatens the profitability of companies.
This article is written for manufacturing leaders to help them understand the full extent of the labor shortage and the reasons behind it in the manufacturing sector. Later, we will highlight ways to combat labor shortage to provide practical solutions for manufacturers.
Statistics and Stylized Facts Regarding Labor Market in Manufacturing
To illuminate manufacturing managers on how to combat the labor shortage, we must first demonstrate the problem’s scope and the underlying reasons why people, particularly Gen Z and Millennials, are not considering careers in factories. Let us begin by examining the stylized facts concerning the labor shortage in the US, which can be applied to other developed economies.
How Deep is the Labor Shortage Problem for Manufacturers?
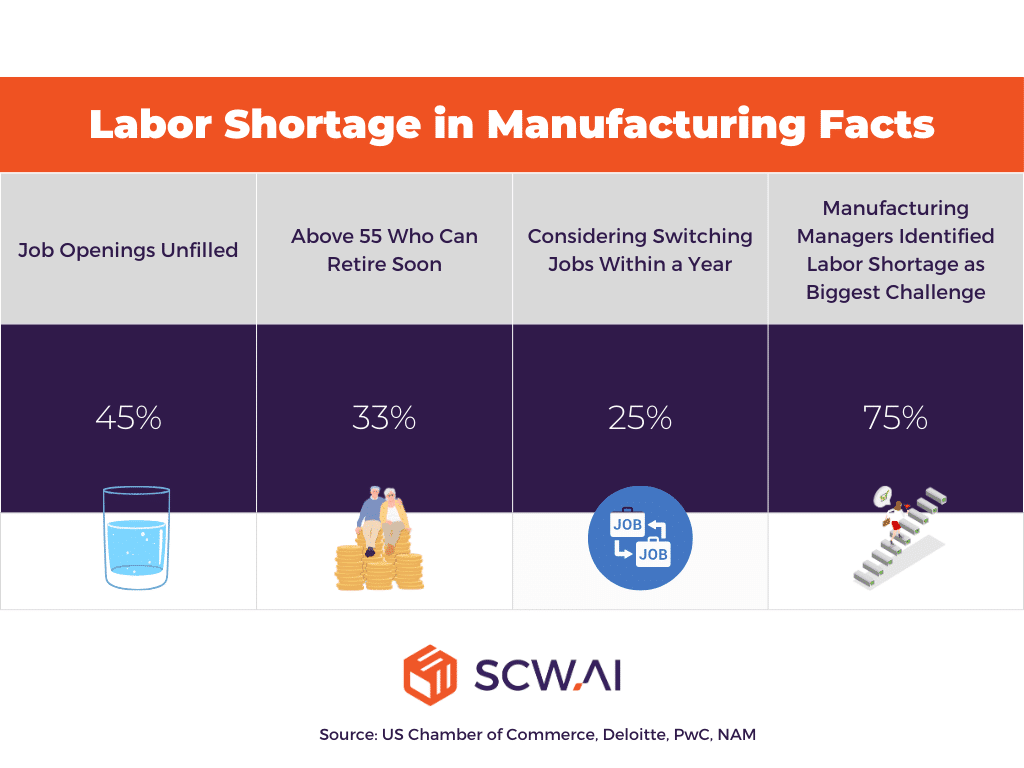
- According to the US Chamber of Commerce, 45% of job openings remained unfilled.
- A Deloitte analysis found that one-third of the manufacturing workforce is over 55 years old, suggesting that the labor shortage problem for manufacturers could become more critical as these baby boomers retire.
- A global scale, 2023 PwC Survey found that a quarter of workers are still considering switching jobs within a year, which can lead to a costly labor skill gap and require additional onboarding processes.
- Nearly 75% of manufacturing managers identified skilled labor shortage as their biggest business challenge, according to a National Association of Manufacturers (NAM) survey.
In light of this evidence, it is safe to predict that labor shortage will continue to be a bottleneck for manufacturers. This necessitates strategic thinking that addresses two key areas:
- Increasing labor productivity: This will allow manufacturers to operate with fewer workers without compromising capacity.
- Understanding the reasons behind the labor shortage and taking action: Manufacturers need to differentiate themselves from competitors to attract talent.
What do the Workers Expect from Manufacturers?
Now, let us explore why workers may find manufacturing careers unappealing or what kind of work environments they prefer.
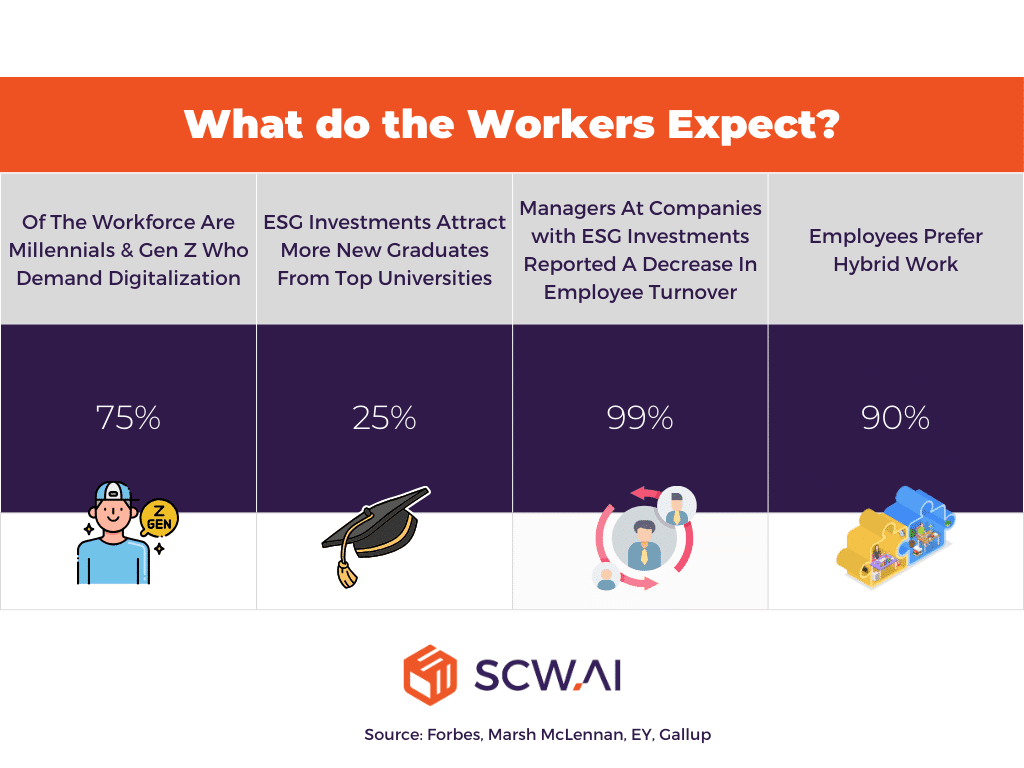
- A recent Gallup survey found that a hybrid work model is the most preferred way of working, with 90% of employees expressing a desire for some level of out-of-office work. The survey also revealed that for roughly 30% of workers, the absence of any remote work options is a dealbreaker, potentially leading them to quit their jobs immediately.
- A Forbes article highlights a key point: Around 75% of the workforce consists of Millennials and Gen Z. These generations grew up with technology and use digital tools for everything from finances to shopping, art exploration, and even social interaction. The article argues that it is naive to believe they would not expect similar tools in their workplace.
- A MIT article found that “Toxic Business Culture,” characterized by disrespectful, abusive, greedy, and exclusionary behavior towards women, LGBTQ+ individuals, and racial minorities, is a stronger driver of job switching for workers compared to compensation and benefits.
- A Marsh McLennan study suggests that companies with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investments attract 25% more new graduates from top universities. Similarly, an EY study found that 99% of managers at companies with ESG investments reported seeing or expecting to see a decrease in employee turnover within five years.
4 Ways to Combat with Labor Shortage in Manufacturing
By utilizing the stylized facts above we come up with four main strategies that will help manufacturers to combat the labor shortage problem.
1. Augment Your Workforce
Workforce augmentation refers to the strategic use of digital tools and technologies like AI, digital twins, IoT and automated dashboards to enhance human capabilities. This approach can help manufacturers combat labor shortages in two ways:
- By making factories more attractive to digital-native younger generations.
- By improving worker productivity, thereby reducing overall workforce needs.
Here are the augmented workforce use cases for manufacturers:
1.1 Automate Tasks
On shop floors, many tasks, like scheduling, are repetitive. Industry 4.0 solutions can significantly reduce the time workers spend on these tasks. For example, a Boston Consulting Group study found that AI-driven Schedulers can cut the time spent by scheduling teams in half. This freed-up time allows teams to focus on other value-added activities or you can operate with less workers.
- Scheduling Automation: AI-driven APS systems can solve job shop scheduling problems significantly faster and more efficiently than human specialists. Additionally, AI schedulers enhance factory agility by allowing managers to select various algorithms that can minimize makespan, maximize OTIF scores, and promote just-in-time delivery, among other benefits (See image below).
- Maintenance Activities Automation: Machine learning-driven predictive maintenance can extend equipment lifespan and improve uptime within the factory by automating maintenance decisions and making maintenance activities proactive.
- Data Collection Automation: IoT tools integrated with PLCs can automatically collect high-quality, real-time data about machines, workers, and the environment. This data can then be used for reporting activities and factory monitoring.
1.2 Organize Customized Training for Your Workers
One way to boost workforce productivity is by organizing training programs tailored to your workers’ specific skill sets. This targeted approach ensures that workers do not waste time in generic training programs if they are already proficient in a particular task.
To develop data-driven training programs, managers need access to labor performance reports that detail worker efficiency for different production tasks (setup, run time, cleanup) compared to planned durations (See Image Below).
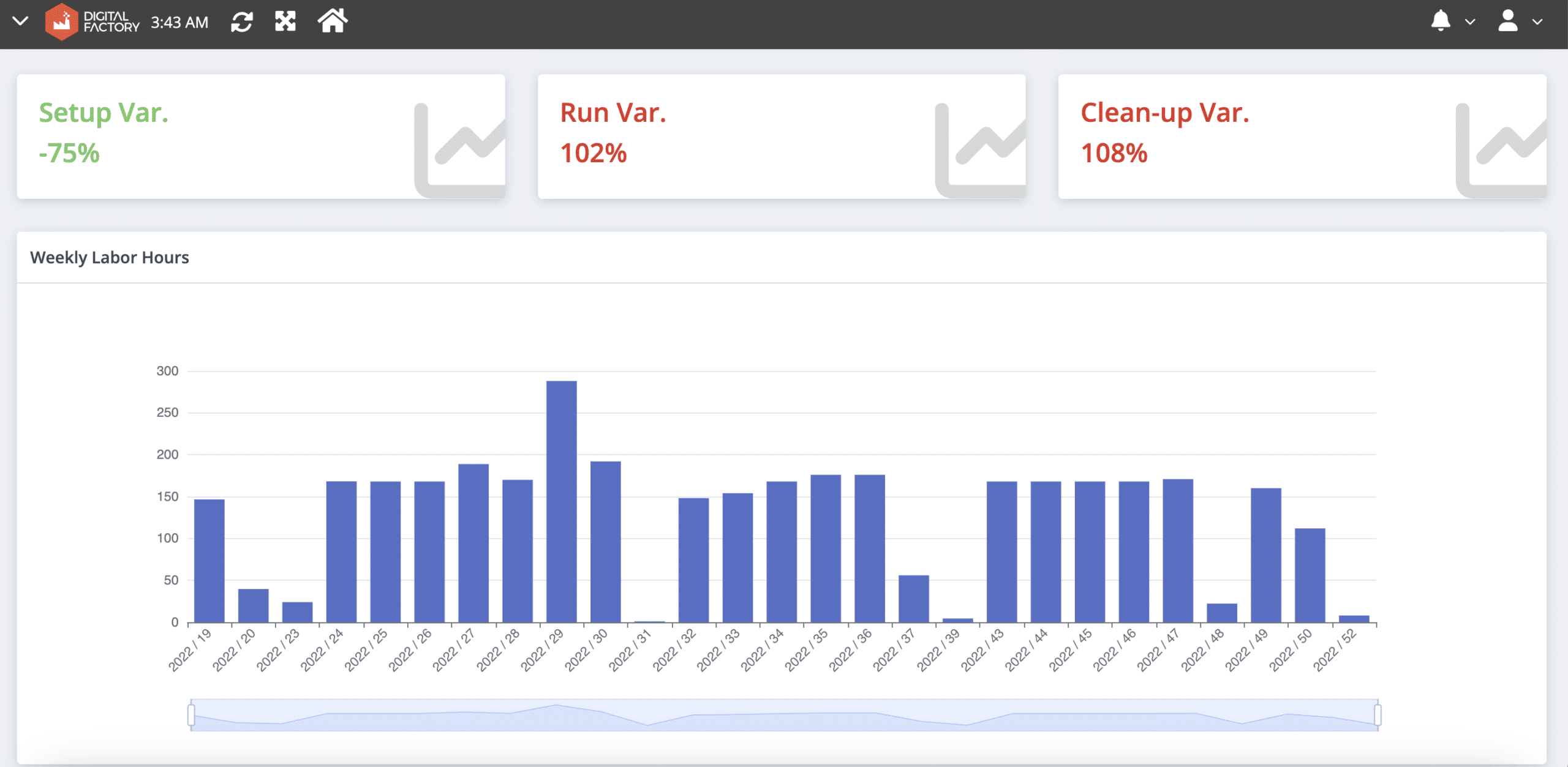
Once you have identified individual training needs through automated reports, digital twins can be leveraged for the training itself. For instance, imagine your workers need training on machine setup. Instead of risking real-machine operation while they hone their skills, they can practice in a safe and realistic simulation of the factory environment using the digital twin.
1.3 Ease Documentation Process via Paperless Manufacturing
A McKinsey study revealed that paper-based documentation processes can consume up to 30% of worker time, particularly in industries like pharmaceuticals where strict adherence to regulations like cGMP is crucial.
Our case studies demonstrate that by implementing paperless manufacturing solutions, the duration of this tedious process can be reduced by 50% to 85%, depending on the specific task and industry. This shift frees up worker time for more value-added and engaging activities.
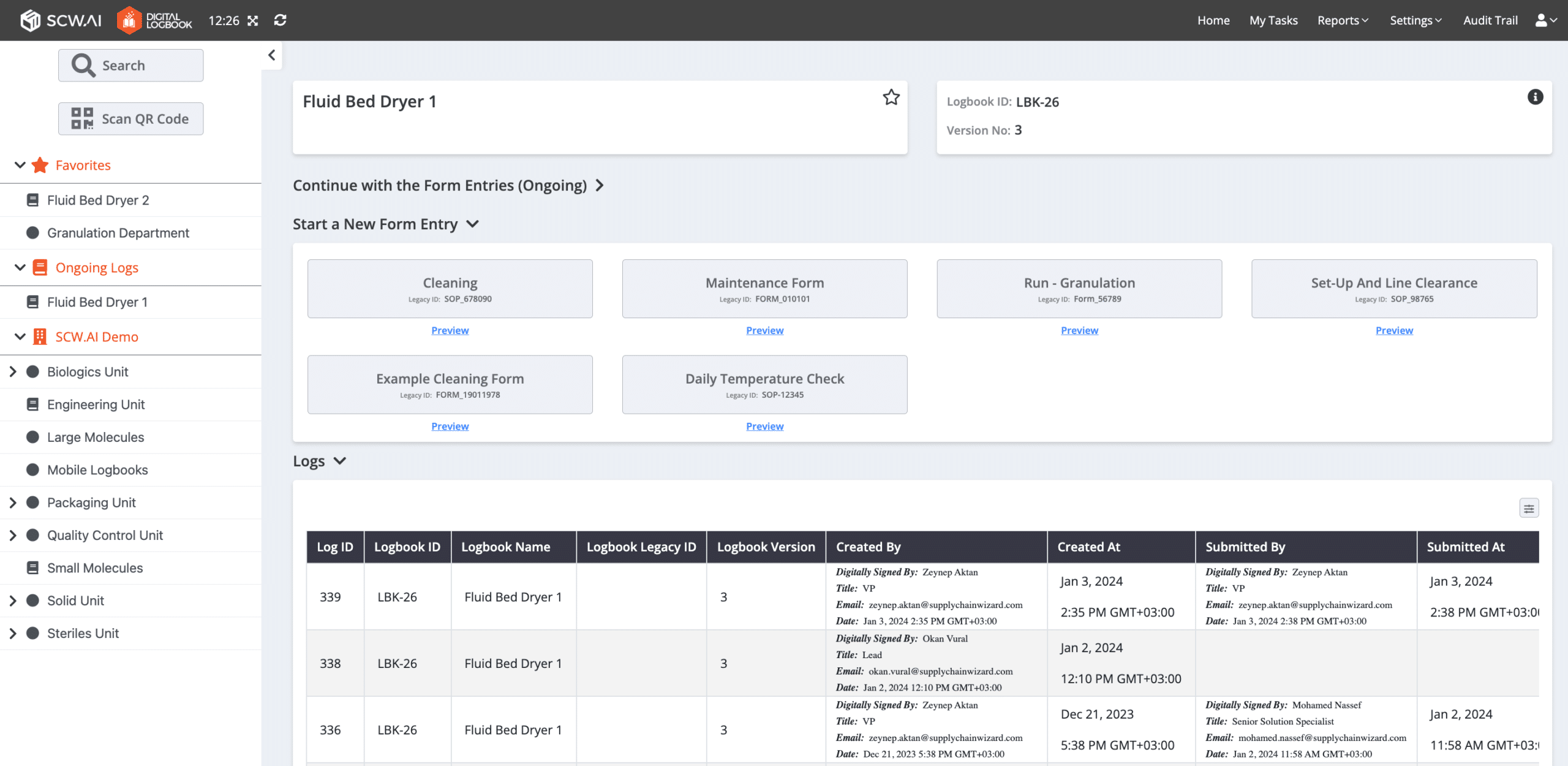
To learn features and use cases of our GMP compliant Digital Logbook read our SCW.AI’s Digital Logbook: Main Features & Use Cases article.
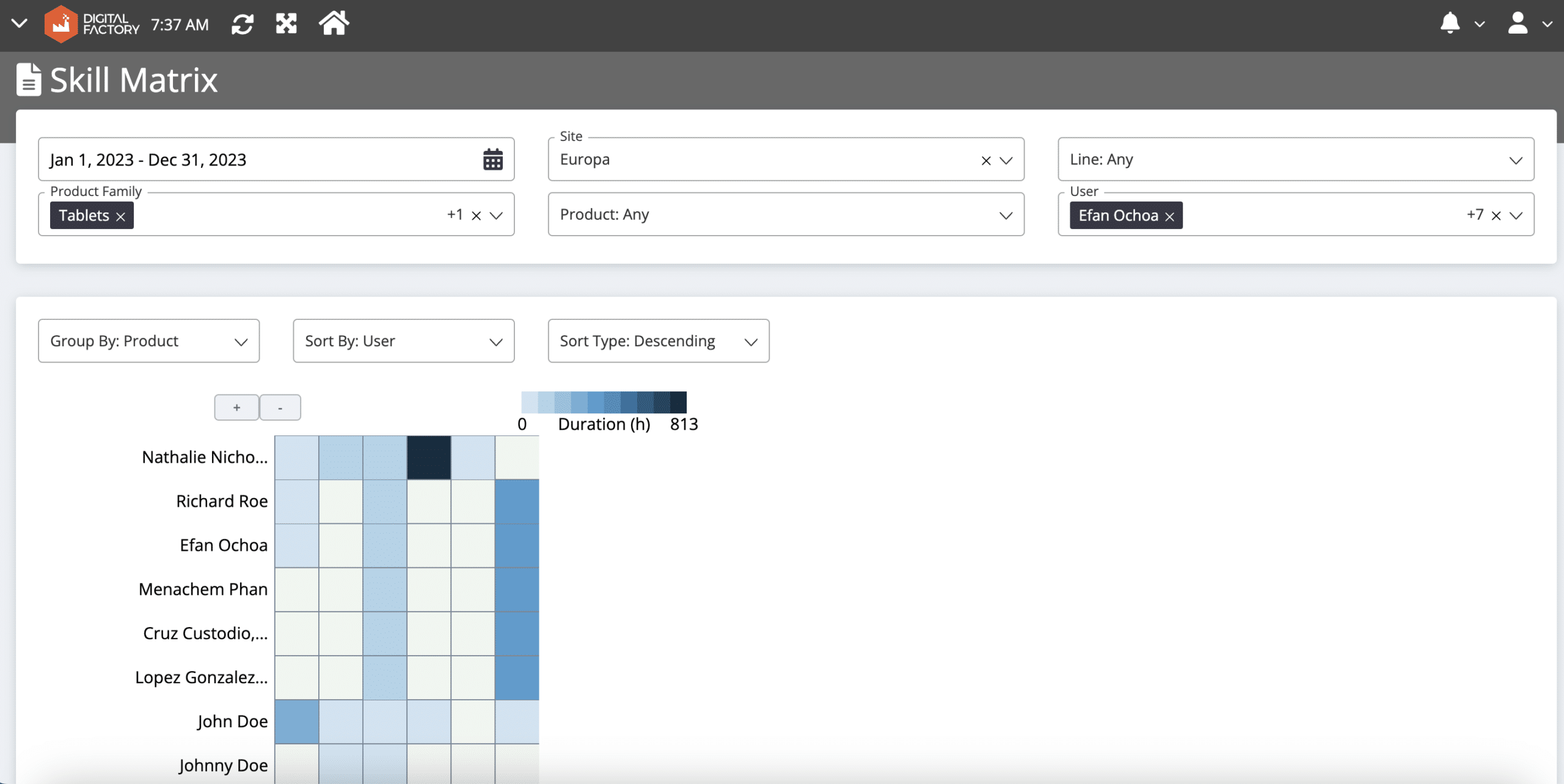
1.4 Schedule Labors by Considering Their Skills and Experience
In factories, a worker’s affinity for the production line, the product itself, and the machinery they operate are crucial factors in improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). To optimize OEE, managers should strategically match workers to production lines based on their skills and experience. Labor skill matrices are a simple yet powerful tool for achieving this. These reports leverage historical data to assess a worker’s capabilities for specific tasks.
2. Invest in ESG
Today’s workforce expects a climate-neutral, inclusive, and fair work environment that supports their reskilling opportunities. However, according to the 2023 Edelman Trust Barometer, there is a general perception that businesses fall short of these expectations (See below image). The study also reveals that a company’s commitment to these values, coupled with demonstrable action, significantly influences the decision-making of nearly 70% of employees when choosing a workplace.
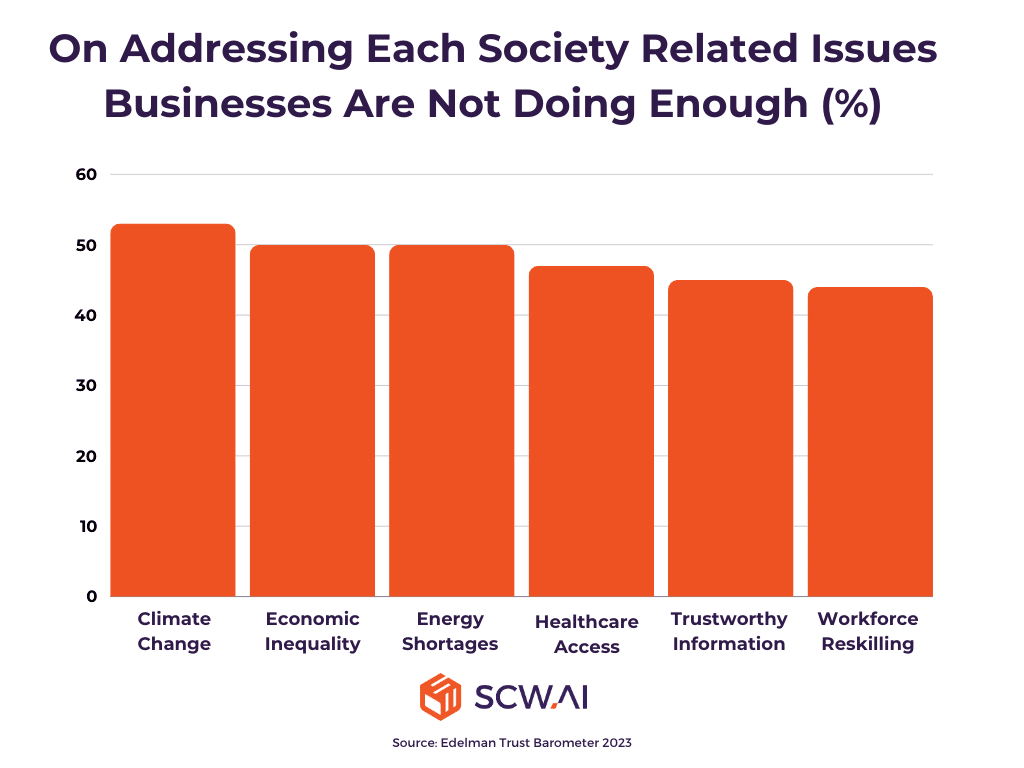
The social issues that are mentioned above all fall under the umbrella of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors. We recommend that companies begin collecting and reporting ESG data for each component, ideally through a third-party verification process. Comprehensive ESG reporting will reveal any shortcomings in your sustainability and fair business practices, allowing you to take targeted actions for improvement. Which in return increases your chance of hiring and retaining skilled employees.
Here are some metrics manufacturers can disclose:
2.1 Environmental Metrics
- Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emission: Equivalent to gasses such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, which are emitted by operational activities of a manufacturing business..
- Emissions Intensity: For a sizable manufacturer, overall corporate carbon emissions are likely to be substantial. Conversely, evaluating emissions intensity by considering emissions per dollar or per product can provide insight into the environmental impact, indicating a company that potentially has a lower ecological footprint.
- Energy Mix: If your factory is located in a region with existing green energy producers, and you source your manufacturing energy from them, or if you have solar panels installed on your roof, your carbon footprint can be significantly reduced, even in the presence of high energy consumption. Therefore, it is crucial to disclose the percentage of corporate energy consumption that is generated from renewable sources.
- Resource Productivity: This metric can be calculated by dividing total sales by the mass of virgin materials used for manufacturing, providing insight into how efficiently manufacturers utilize and replenish materials sourced from the Earth.
- Percentage of Circular Water Consumption: The industrial organizations are heavily dependent on water. On the other hand water is a scarce resource where many populated regions from all continents deal with extreme risk of reaching healthy water. Hence, possessing water treatment systems that enable companies to reuse a certain percentage of water for their activities is a crucial metric.
2.2 Social Metrics
Measuring and enhancing social metrics is instrumental in mitigating employee turnover. Here are some recommended metrics for disclosure:
- CEO Pay Ratio: This ratio is calculated by dividing the CEO’s total earnings, encompassing bonuses, by the company’s median compensation. A higher ratio indicates a less equal distribution of turnover, potentially leading to employee dissatisfaction.
- Gender Diversity: This represents the ratio of men to women employed by a company.
- Gender Pay Ratio: This metric is determined by dividing the median male earnings in a company by the median female earnings. It is a crucial statistic for stakeholders assessing occupational segregation within the organization.
- Injury Rate: This metric illustrates the frequency of injuries occurring in a factory.
2.3 Governance Metrics
- Board Gender Diversity: This signifies the ratio of men to women among board members.
- Incentivized Pay: This metric signifies the presence of corporate policies that reward employees for enhancing the ESG posture of the business through bonuses. For example, a scheduling team with an incentivized pay aimed at reducing the company’s GHG emissions by 3% without compromising output and cycle time. Successful achievement of this goal results in predetermined awards for the team.
- Supplier Code of Conduct: The constitution of a firm outlines the standards it seeks when engaging in business with other companies. As part of a supplier code of conduct, certain international certificates, ESG reports, product carbon footprint metrics, and similar criteria can be stipulated as prerequisites for considering collaboration with a specific company.
- External Audit: Demonstrating your willingness to undergo external audits signifies the company’s commitment to transparency and is regarded as a commendable ESG practice. (For manufacturers obligated by CSRD, this is a mandatory requirement.)
- Anti Corruption Practices: To showcase fair operating practices and high standards against corruption and bribery, consider obtaining international certifications such as ISO 26001 and ISO 37001.
3. Make Your Factory a Hybrid Work Environment
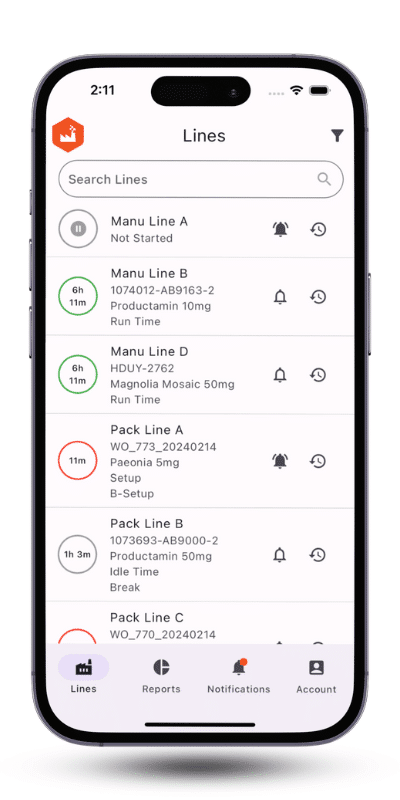

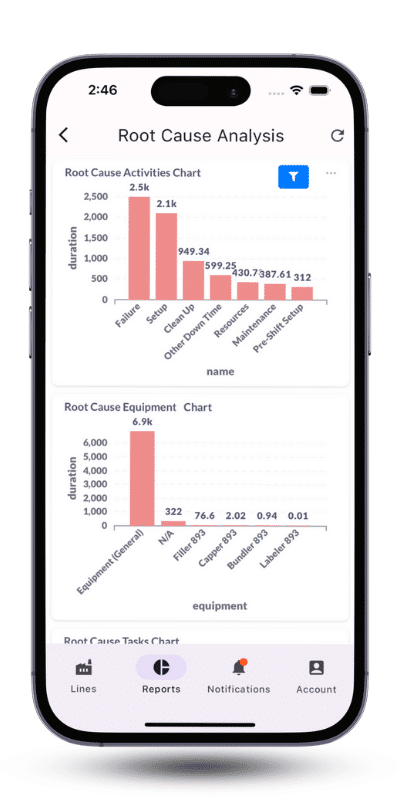
By embracing a hybrid work model, you can attract and retain top talent who value work-life balance and remote work options. This does not mean factory workers will be abandoning the shop floor entirely. But for administrative tasks, planning, and communication, remote work can be a reality.
The key to success lies in leveraging technology. Real-time dashboards and manufacturing apps provide constant visibility into production from any location. These tools allow remote engineers to monitor machines and lines, identify issues, and collaborate with colleagues in real-time, ensuring a seamless workflow even with a hybrid workforce.
4. Provide Career Building Opportunities
By offering mentorship programs, skills training, and opportunities for internal job shadowing, you demonstrate your commitment to their professional growth. This not only benefits them by developing their skill sets but also strengthens your talent pipeline by creating a pool of qualified candidates for future openings. This not only empowers employees but also demonstrates your commitment to a modern and adaptable work environment.
For European Pharma manufacturers we published a new eBook called: Bridging Europe’s Pharma Productivity Gap with Digital Factory Transformation. By downloading it you can learn how pharma 4.0 transformation can stop negative impact of labor shortage and many more issues that cause productivity gap. Download EU pharma eBook Now!
Minimize the Negative Impacts of Labor Shortage with SCW.AI
SCW.AI’s Digital Factory Platform empowers manufacturers to augment their workforce. Leverage rich insights into shop floor activities through digital reports and dashboards of Labor Tracker like Labor Performance and Labor Skill Matrix. Paperless quality solutions such as Digital Forms and Logbook streamline reporting, while AI-powered scheduler automates planning and tasks like labor scheduling.
Gain real-time factory visibility through connected IoT devices. Optimize profitability and sustainability with OEE Tracker, which guides managers in allocating resources effectively. Finally, engineers can monitor production and line status conveniently via the Digital Factory Wizard mobile app.
To learn more about Digital Factory Platform and our value proposition, book a demo now.
To learn more about labor shortage in manufacturing sector and and digital solutions to mitigate it; contact us.