According to McKinsey, digital transformation in manufacturing can boost throughput by 10% to 30%, improve cost of quality by 10% to 20%, and cut machine downtime by up to 50%. Despite these benefits, a PwC study found that only one-third of manufacturers have progressed beyond the planning or initial stages of digital transformation, missing significant opportunities.
This slow adoption is often due to a lack of knowledge about digital transformation in manufacturing. This article addresses this gap by detailing the benefits, showcasing top solutions, presenting real-life examples, and highlighting key trends to help managers succeed in their digital transformation efforts. At the end of the article, we introduce our Digital Factory Platform, offering end-to-end factory automation to support your transformation journey.
What is Digital Transformation in Manufacturing?
Digital transformation in manufacturing involves replacing paper-based or manual processes with digital tools and automation technologies to generate business value. Key business goals include:
- Cost reduction
- Quality and compliance enhancement
- To achieve greater resilience and flexibility
- Sustainability improvement
- Employee retention and productivity improvement
To achieve these goals, various technologies can be utilized:
- IoT: Collects shop floor data in real-time.
- Manufacturing Analytics: Displays real-time data on automated reports and dashboards, enabling executives to make data-driven decisions.
- AI Solutions: Automates decision-making processes or augments decision-makers’ capabilities to achieve better outcomes.
- Action Trackers: Enhances organizational and management capabilities by providing dedicated dashboards that show trends of main manufacturing KPIs, detected issues, and personnel responsible for addressing these issues.
- Paperless Manufacturing Solutions: Replaces paper-based reporting, which is time and resource-intensive, with easy-to-use digital forms, logbooks, and batch records.
Top 6 Benefits of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
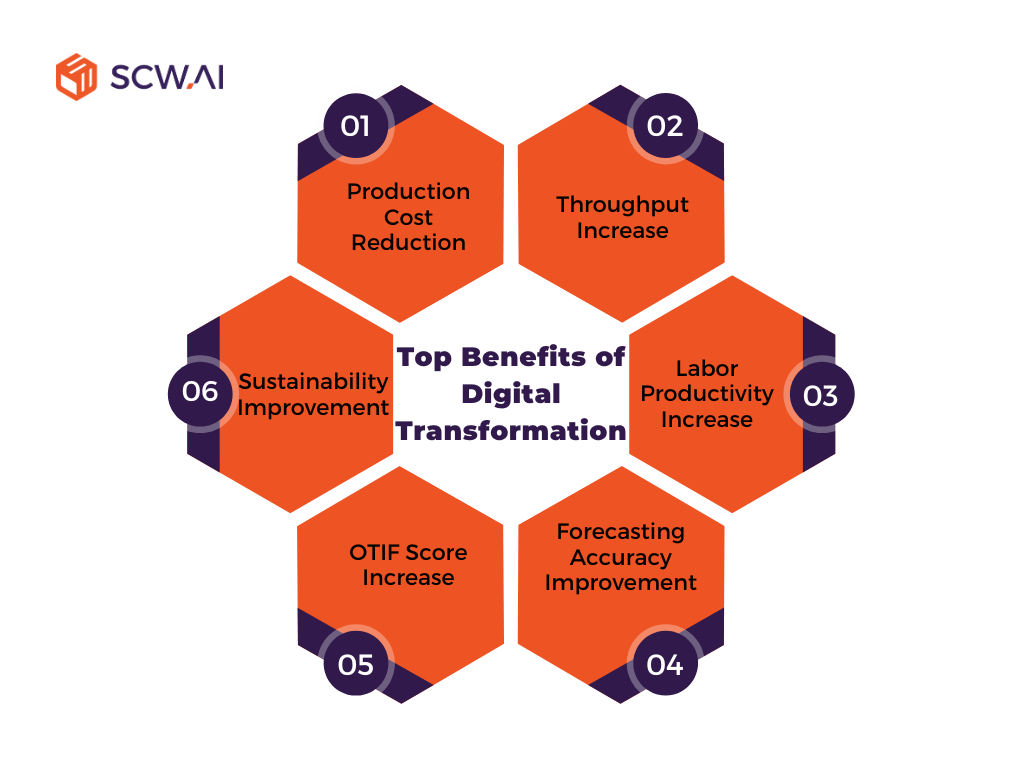
1. Production Cost Reduction
According to a World Economic Forum (WEF) study, digital factory transformation has reduced production costs by up to 70% in some cases. For the majority of manufacturers, cost reductions typically range between 15% and 30%, illustrating the significant impact of digital transformation on profitability.
Cost reduction via digital transformation can occur variety of reasons:
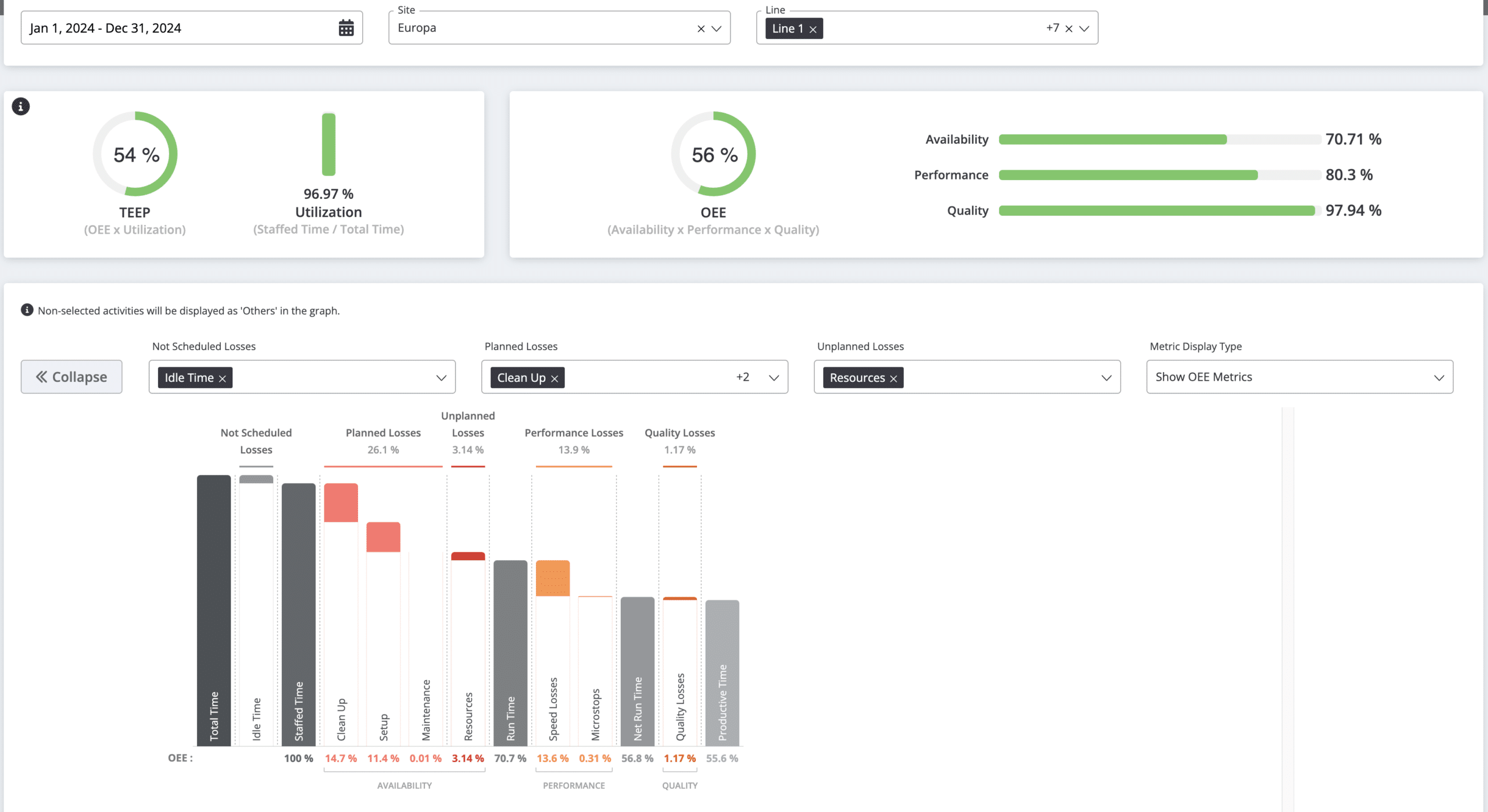
- Improved Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): Increased visibility allows for addressing production bottlenecks.
- Increased First Pass Yield: Reduction in scrap rate and units require rework thanks to automation pave roads for world class manufacturing.
- Enhanced Job Shop Scheduling: Reduces cycle time.
- Effective Issue Detection and Tracking: Enables faster corrective actions and many more.
2. Throughput Increase
According to the WEF‘s study, many factories have more than doubled their productivity thanks to digital transformation. Similar to cost reduction, various factors can positively impact throughput, such as optimal line balancing, changeover minimization, and effectively eliminating micro stops.
3. Labor Productivity Increase
According to a McKinsey analysis, digital transformation in manufacturing increases labor productivity by 15% to 30%. Key reasons for this include:
- Reduction in manual tasks, allowing workers to focus on value-added activities.
- Augmentation of workers through AI/ML models.
- Greater visibility of operators via RFID cards, improving allocation.
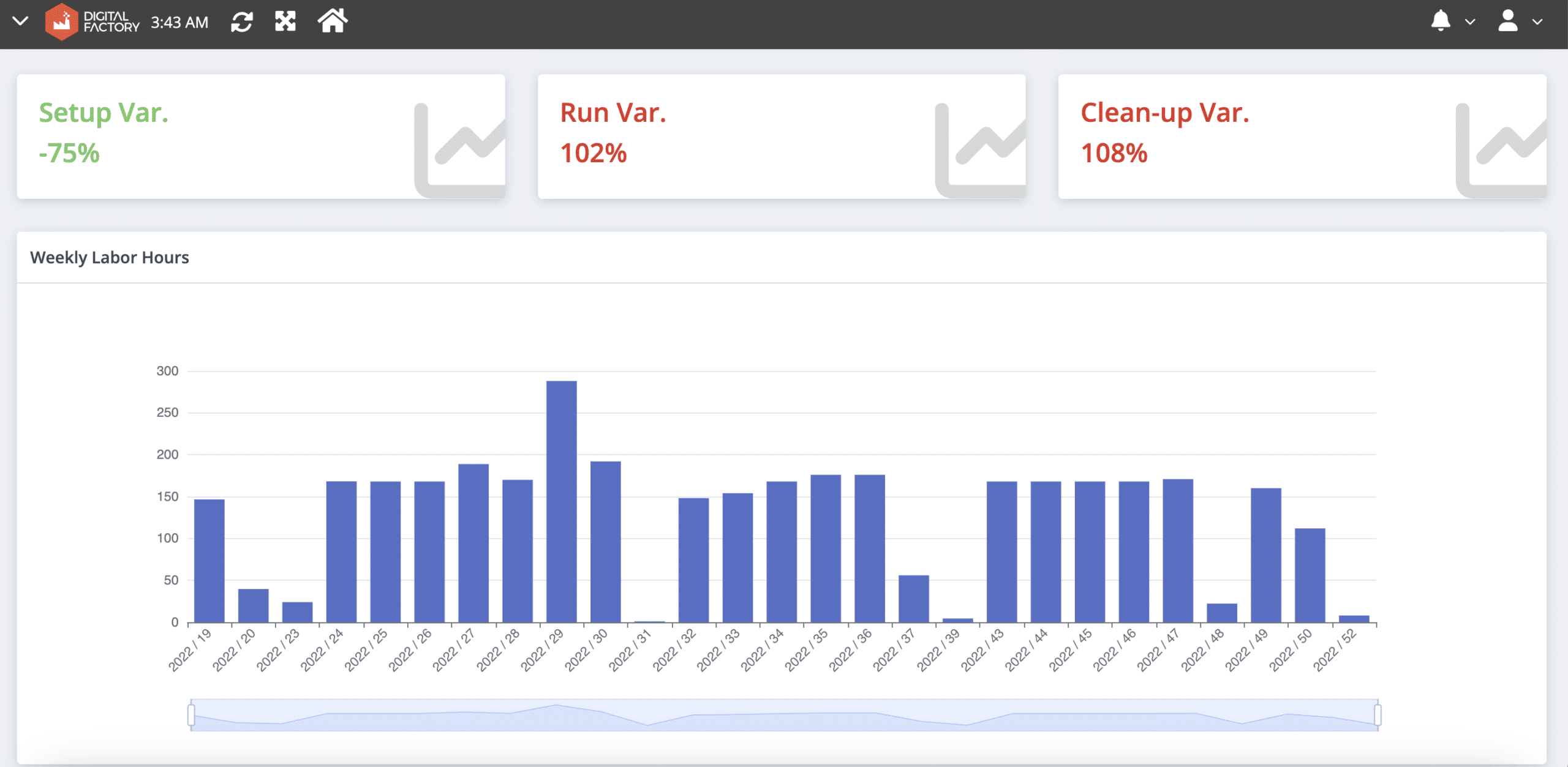
- Labor performance reports and skill matrices (See image below) , providing data for optimal labor scheduling.
4. Forecasting Accuracy Improvement
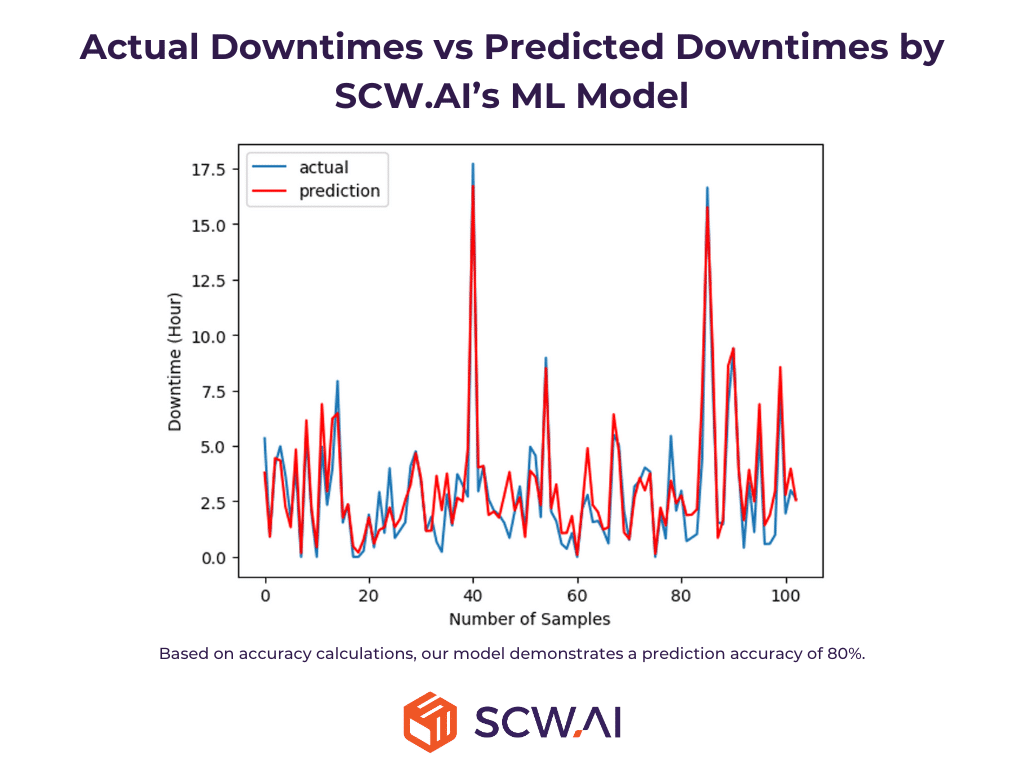
According to McKinsey, digital transformation improves forecasting accuracy for manufacturers by 85%. This is due to advanced planning and scheduling systems that offer real-time data on raw material flow, capacity use, and schedule adherence but most importantly machine learning models with impressive computational power.
For instance, in the video below, Tolga Kula, Global Head of Integrated Business Planning at Merck Group, explains how artificial intelligence improves forecasting capabilities for pharmaceutical manufacturers and comes up with superior results compared to human planners.
To learn more about Pharma 4.0 and its adoption strategies you can listen/watch SCW for Pharma podcast series.
5. OTIF Score Increase
According to the WEF, digital transformation improves OTIF (On-Time In-Full) scores by around 10 percentage points on average. This improvement is crucial, as Forbes highlights that OTIF penalties can cost medium-sized businesses around $350k, significantly impacting profitability. The main reasons for OTIF improvement include achieving optimal takt time through automation and enhanced shop floor visibility.
6. Water Consumption and Carbon Emissions Reduction
Based on the reports of the WEF, digital transformation in manufacturing can reduce CO2 emissions and water consumption by approximately 15% on average. This reduction is primarily due to the use of sustainability software, such as carbon trackers, which provide visibility into the environmental impact of factories, enabling management to take data-driven actions. Additionally, the implementation of digital lean strategies reduces waste, further decreasing the negative environmental impact of factories.
Top 5 Digital Manufacturing Solutions
1. IoT
The first step in digital factory transformation, whether the goal is deploying manufacturing analytics or AI models, is the automated collection of real-time granular shop floor data. IoT automation facilitates this initial step using sensors, smart devices, and utilizing technologies such as RFID, Bluetooth, WiFi and more. This approach enables manufacturers to collect:
- Machine data: Including heat, vibration, and electric current. Integrating IoT devices with Modbus PLCs is crucial for such data collection.
- Production data: Including counts of good units and defects, which are essential for station-level production tracking and calculating numerous manufacturing KPIs.
- Labor data: Allowing manufacturers to track which operators are on duty on specific workstations.
2. Manufacturing Analytics
Manufacturing analytics involves the use of data analytics tools to transform raw production data into actionable insights. These tools help in identifying trends, detecting anomalies, and making data-driven decisions.
Manufacturing analytics can be deployed for various purposes, including:
- OEE Waterfall Analysis (See image below)
- Changeover Analysis
- Labor Performance Analysis
- Schedule Adherence Analysis and many more.
3. AI Solutions for Manufacturers
AI solutions for manufacturers can be grouped into three main categories, as illustrated in the image below.
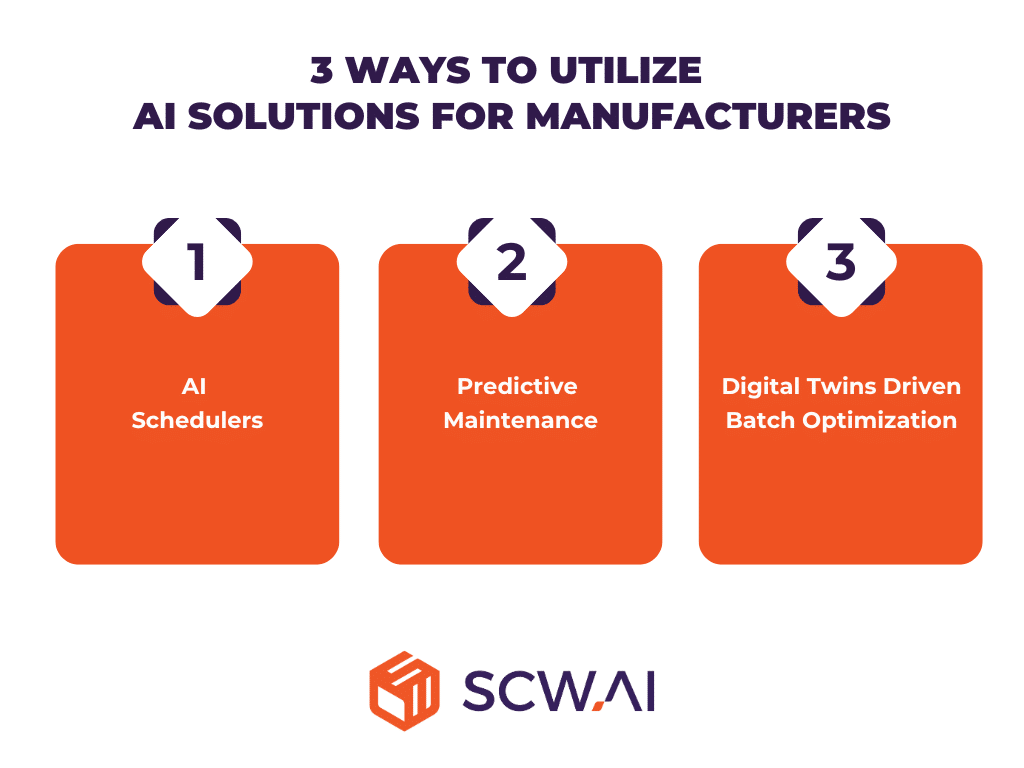
3.1 AI Schedulers
AI schedulers automate job shop and labor scheduling more efficiently than human schedulers. A Boston Consulting Group study also highlights these models speed up scheduling phase by reducing schedulers’ tasks by half through automation.
AI scheduling software offer agile manufacturing solutions for various optimization scenarios, depending on your business needs, such as:
- Just-in-Time Scheduling: Minimizes inventory and ensures product freshness, crucial for the food and beverage sector.
- Changeover Time Minimization: Reduces changeover times, essential for highly regulated industries like pharmaceuticals, where line cleaning consumes significant time.
- Cost Minimization: AI models optimize scheduling to reduce costs by considering each manufacturer’s unique cost functions.
3.2 Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a digital total productive maintenance strategy that schedules maintenance activities before equipment failure, by optimizing the duration of planned maintenance. According to a Deloitte study, this cutting-edge strategy increases factory productive time by 10% to 20%.
3.3 Digital Twins Driven Batch Optimization
Digital twins enable manufacturers to simulate production with different parameter values. By analyzing these simulations, executives can discover optimal machine setups and workforce organization to maximize processes. This approach helps reduce cycle times, improve product quality, minimize costs, and more. For instance, a Singapore-based manufacturer reduced production costs by 25% using a factory twin.
A quick way for manufacturers to build a digital twin is by using generative AI. For more details, you can read our In-Depth Guide to Generative AI in Manufacturing article.
To explore more about AI technology and its unique applications for manufacturers, check out our Top 5 AI Use Cases in Manufacturing article.
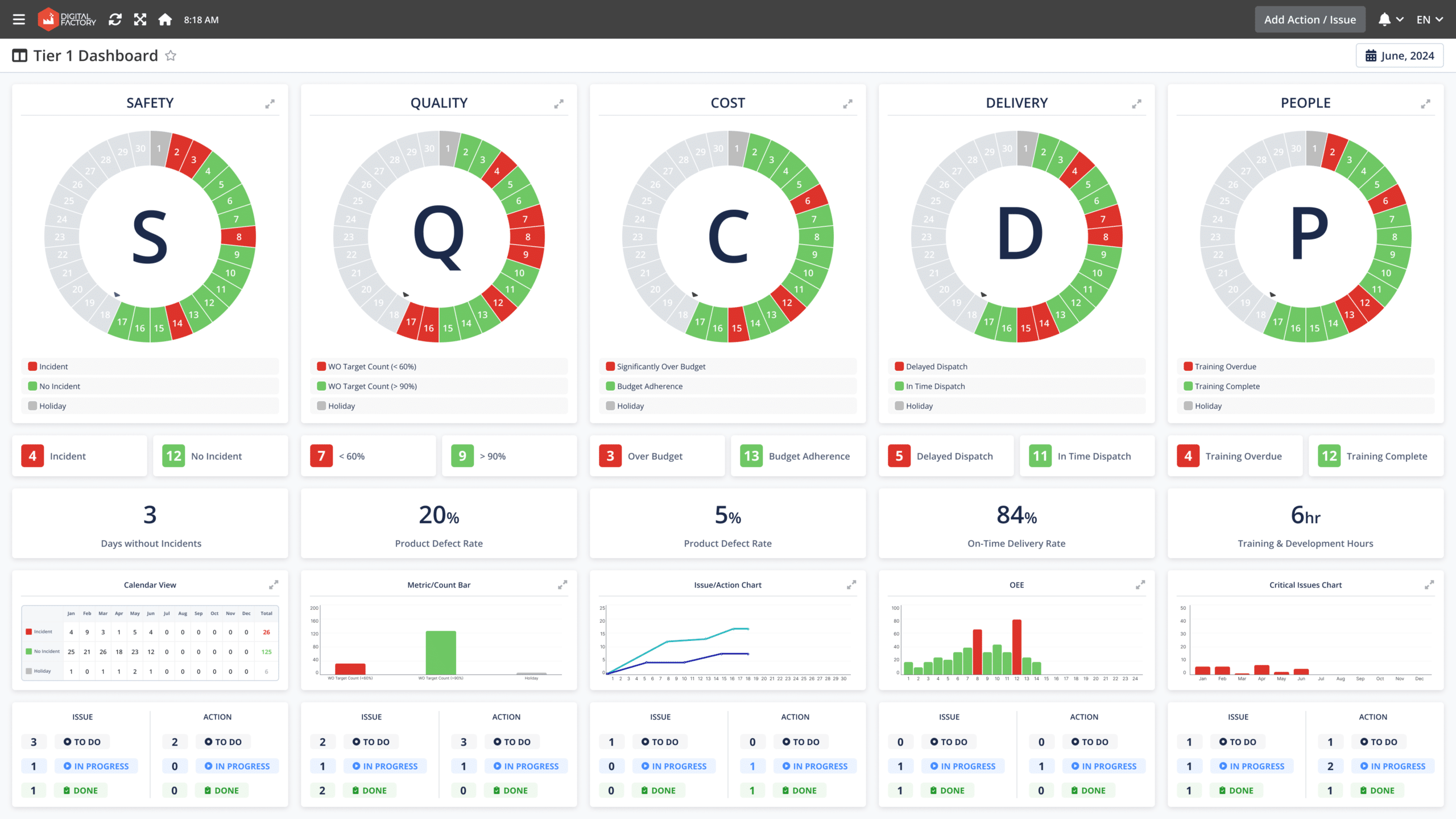
4. Digital SQCDP Boards and Action Trackers
Many manufacturers use whiteboards with the SQCDP (safety, quality, cost, delivery, people) framework as a daily routine to assess current bottlenecks and plan next steps. However, this traditional method often leads to organizational and management inefficiencies because bottlenecks can be invisible to the management team, and it is difficult to monitor if action items are implemented.
Digital SQCDP boards solve this issue by displaying the most crucial KPIs for daily operations. With color-coded visualization, issues can be detected at a glance. Once issues are identified, these tools enable managers to create tasks, assign responsible individuals, and set deadlines, facilitating effective execution of decisions.
5. Paperless Manufacturing Solutions
Due to compliance or quality concerns, manufacturers often document their activities. However, filling paper documents is a time-consuming task for operators and line leaders, causing inefficiencies in work order management and slowing down production. Additionally, paper production incurs environmental costs, such as deforestation, high water consumption, and CO2 emissions.
Paperless manufacturing solutions provide a user-friendly interface that speeds up the documentation process. Storing data digitally makes it easier to retrieve when needed for analysis or audits. Furthermore, it eliminates the need for paper, supporting sustainability initiatives in factories.
For regulated industries like pharmaceuticals, there are specialized paperless quality solutions called Digital Logbooks. These tools are designed to adhere to ALCOA+ data integrity principles and cGMP rules, thereby improving compliance with regulations.
5 Digital Transformation Examples in Manufacturing
1. A Case Study in Kordsa's End-to-End Factory Digitization
Kordsa, a global leader in sustainable reinforcement solutions, operates facilities in seven countries. To enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and support their sustainability initiatives, Kordsa aimed to automate and or augment data gathering, interpretation, and decision-making processes.
To achieve these goals, they partnered with us and utilized various modules of our Digital Factory Platform, including:
As a result, Kordsa significantly reduced unplanned downtime, improved predictive capabilities, and decreased non-value-added labor tasks by 30%. To learn more about Kordsa’s digital factory transformation journey, watch the video below.
You can also download the PDF about Kordsa/SCW case studies to learn more about.
2. Sterile Pharmaceutical Manufacturer Reduced Downtime 30%
One of the world’s largest sterile pharmaceutical CDMOs faced significant challenges with unplanned downtime and root cause analysis due to limited visibility and heavy reliance on paper-based processes. To digitize their factory, they partnered with us and implemented our OEE Tracker, Labor Tracker, and Asset Tracker solutions.
By effectively tracking equipment and labor, the company was able to identify the root causes of unplanned downtimes. This data-driven, real-time decision-making approach led to a 30% reduction in unplanned downtime and a significant increase in productivity.
To find out more about this digital transformation example you can download its dedicated PDF document.
3. Food Manufacturer Cut Production Costs by 20% with AI Scheduler
Manufacturers often overlook that scheduling problems are categorized as Non-Deterministic Polynomial Time problems. This means that current mathematical models do not offer optimal solutions, and finding near-optimal solutions for scheduling problems requires high computational power, an area where computers excel. The following digital transformation example in manufacturing illustrates this point.
In a regular meeting with our customer success team, a food manufacturing customer was asked, “Why don’t you use our AI Scheduler? It can be significantly beneficial by automating job shop scheduling for JIT delivery, changeover minimization, and cost minimization.” The response was, “Our schedule is already optimal; we do not need any AI assistance for job shop scheduling.”
To test their hypothesis, we offered a free demo that orchestrated their work order by considering their cost function and constraints. As an initial step, they wanted to see our AI model’s effectiveness in cost minimization, and the results were surprising.
Our AI model consistently found scheduling combinations that reduced costs by around 15% to 20%. Following the success of the test, they added our AI scheduler to their arsenal of digital solutions, significantly reducing costs by executing AI-generated schedules.
4. Pharma Manufacturer Reduced Changeover Time 40%
Changeover durations tend to be longer for pharmaceutical manufacturers because cGMP rules require extensive line cleaning and setup processes. Typically, manufacturers address this by scheduling the same product families consecutively and providing constant worker training to reduce changeover times.
However, successfully executing these plans requires granular visibility into changeover activities. By comparing actual and planned changeover times and having detailed visibility of changeover performance by machine and operator level, managers can develop effective strategies.
One of our pharmaceutical customers utilized our Changeover Analysis tool and within six months, they were able to reduce changeover times by around 40%.

AI is a powerful tool for pharma manufacturers seeking to minimize changeover time. For example, Cipla achieved a 21% reduction in changeover time using AI-powered smart scheduling. Explore more case studies, challenges, and opportunities in our free white paper on AI in pharma.
5. Global Pharma CDMO Achieves 85% Reduction in Log Entry Time
Another major pharmaceutical company aimed to reduce the time required for data entries in logbooks, which must be documented according to ALCOA+ data integrity principles to avoid regulatory penalties.
To achieve this, they implemented our GMP-compliant Digital Logbook. This solution, featuring a digital interface and smart form functionalities such as automatic calculations, conditional workflows, and integration with IoT devices and ERP/MES/LIMS systems, enabled the company to reduce data entry times by 85%.
In addition to reducing data entry and archiving time, they centralized their documents, making them better prepared for audits.
Top Digital Transformation Trends in Manufacturing
In this section, we will highlight the top 4 digital transformation trends in manufacturing to guide managers in their investment decisions.
1. Two-Thirds of Manufacturers Remain in the Early Stages of Digitalization
According to a PwC survey, two-thirds of manufacturers have completed less than 50% of their digitalization journey. This implies that they are either in the stages of developing a roadmap for digital transformation, just beginning it, or making initial progress. The low adoption rate of digital transformation in the manufacturing sector suggests there are still many opportunities for significant business value. With even basic steps, manufacturers can achieve substantial improvements and competitive advantages.
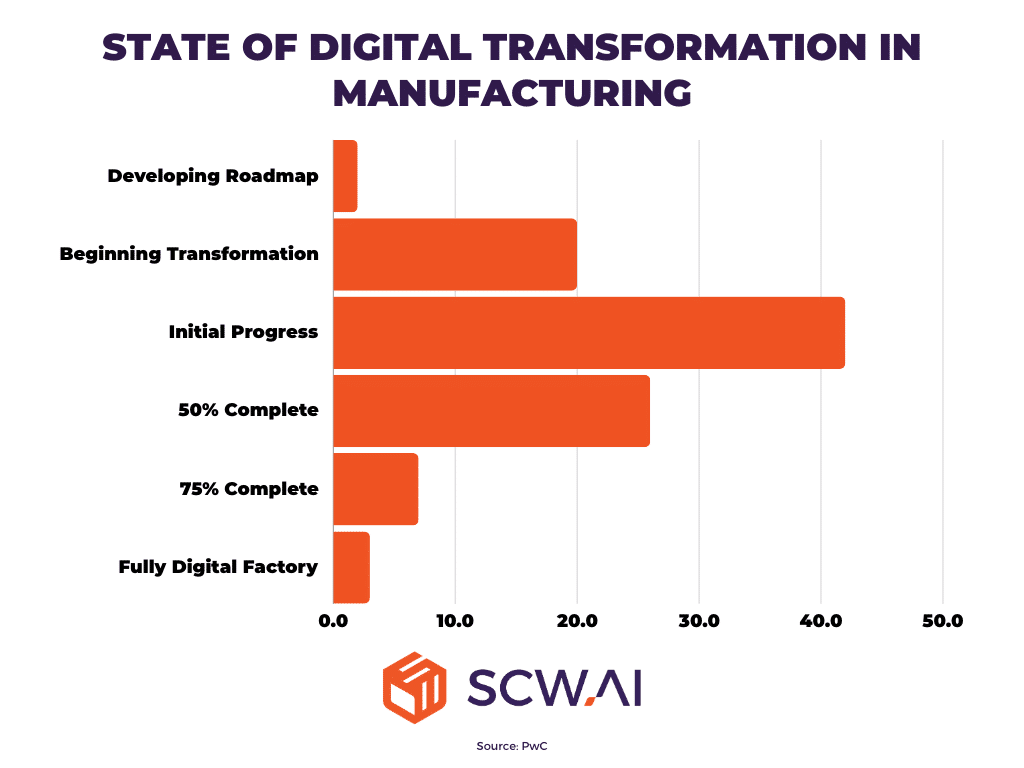
2. Shifting Priorities: Resilience, Flexibility, and Sustainability Gain Importance over Cost
According to a PwC survey, the primary motivation for manufacturers investing in digital tools is now to become more resilient and flexible against business disruptions, rather than merely minimizing costs. Additionally, digitization initiatives aimed at building sustainable factories have risen by around 150% compared to previous years.
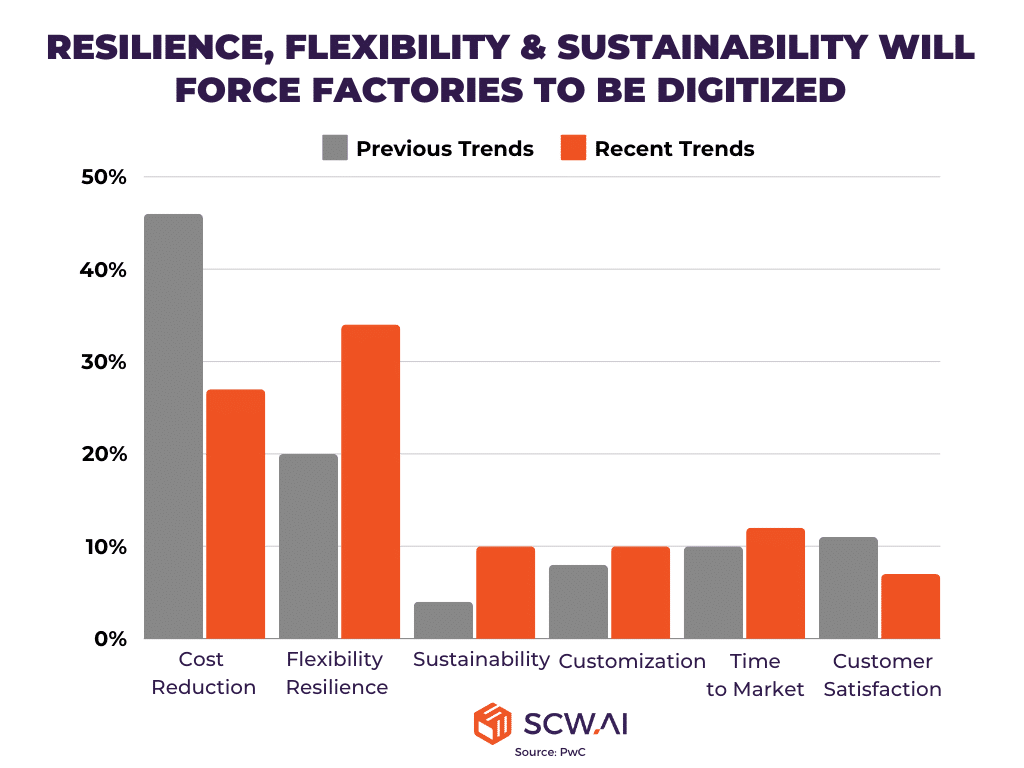
This shift in motivation is understandable. The return of war to Europe and the Middle East, along with increasing political tensions globally, has caused fluctuations in commodity prices and uncertainties in traditional supply chains. New tariffs and trade restrictions further limit global trade. Moreover, sustainability regulations like the CSRD will start impacting many businesses in 2024.
3. Higher Investment Proportion to Revenue Leads Higher ROI
PwC’s study suggests that manufacturers who allocate 3% or more of their revenue to digital transformation are 2.5 times more likely to achieve higher returns on investment. This is because such investments typically deploy more tools across various use cases, creating a positive feedback loop. In contrast, the study found that, on average, manufacturers invest only 1.8% of their net revenue in digital transformation, indicating that many are not using their budgets effectively.
4. Collaboration with Technology Vendors is the Primary Digital Transformation Strategy for Manufacturers
According to Deloitte, six out of ten manufacturers partner with technology vendors for their factory transformation. Given the labor shortage of skilled workers in manufacturing, along with the associated costs and scalability issues, partnering with a technology provider is a sensible approach.

We prepared a comprehensive eBook for European pharma manufacturers on closing productivity gap with digital transformation. Report includes a actionable road map for end-to-end transformation. To learn more download eBook now!
Transform Your Factory with SCW.AI
SCW.AI’s Digital Factory Platform offers comprehensive digitalization opportunities for manufacturers through IoT tools, manufacturing analytics, paperless manufacturing solutions, Digital SQCDP boards, and cutting-edge AI solutions.
If you want to learn more about our value offering for digital factory transformation contact us.
To experience our Digital Factory Platform firsthand, book a demo now.